Modeling lactate threshold in cycling-influence of sex, maximal oxygen uptake, and cost of cycling in young athletes
- PMID: 40220138
- PMCID: PMC12354541
- DOI: 10.1007/s00421-025-05744-y
Modeling lactate threshold in cycling-influence of sex, maximal oxygen uptake, and cost of cycling in young athletes
Erratum in
-
Correction: Modeling lactate threshold in cycling-influence of sex, maximal oxygen uptake, and cost of cycling in young athletes.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2025 Aug;125(8):2159. doi: 10.1007/s00421-025-05890-3. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40759837 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
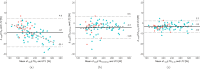
Purpose: Understanding physiological determinants of lactate threshold 2 (LT2) is crucial for tracking adaptations and deriving individualized training recommendations in cycling. Therefore, the study investigated: 1. the accuracy of modeling power output at LT2 in young athletes of both sexes using maximal oxygen uptake ( ), fractional utilization of (% ), and oxygen cost of cycling (Cc); 2. the influence of Cc determination on the model accuracy; 3. the influence of the model predictors and inclusion of maximal lactate accumulation rate ( ) on power at LT2 depending on sex.
Methods: Eighty-three cyclists and triathletes (22 females, 61 males; age [median and IQR]: 14.6 [13.8-17.6] years, [mean ± SD]: 59.2 ± 6.5 mL⋅kg-1⋅min-1) performed an incremental test to determine power at LT2, % at LT2, and Cc (assessed at 3 W⋅kg-1, 75% and 90% LT2).
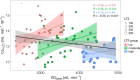
Results: Modeled and experimentally determined power at LT2 demonstrated excellent agreement for all, male and female athletes (ICC 0.961), with Cc at 90% LT2 providing the highest accuracy (ICC 0.986). The three physiological determinants explained 98% of the variance in power at LT2, with the largest unique contribution from (62 and 67% of total ), followed by Cc (8 and 34%) and % at LT2 (5 and 12%) in males and females, respectively, while did not improve the regression.
Conclusion: % at LT2 and Cc accurately predict power at LT2 in young cycling athletes independent of sex, with determination of Cc at 90% LT2 providing the highest accuracy. While contributes most to LT2 in both sexes, Cc appears more important in young females.
Keywords: Aerobic capacity; Endurance performance; Gross efficiency; Maximal lactate accumulation rate; Maximal metabolic steady state; Performance diagnostics; Youth athletes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest. No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

