m6A reader IGF2BP1 facilitates macrophage glycolytic metabolism and fibrotic phenotype by stabilizing THBS1 mRNA to promote pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 40220148
- PMCID: PMC11993514
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-025-05673-1
m6A reader IGF2BP1 facilitates macrophage glycolytic metabolism and fibrotic phenotype by stabilizing THBS1 mRNA to promote pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
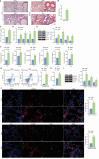
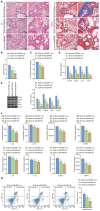
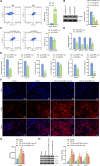
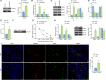
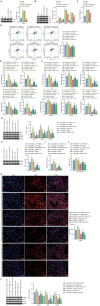
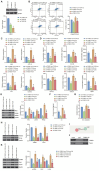
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification, a dynamically reversible epigenetic mechanism, is implicated in pulmonary fibrosis (PF) progression. The function and molecular mechanisms of m6A reader, insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) in PF remain elusive. This study investigates the mechanistic contributions of IGF2BP1 to PF development. We found IGF2BP1 was overexpressed in macrophages of PF mice. IGF2BP1 knockdown markedly attenuated bleomycin (BLM)-induced lung pathology, as evidenced by reduced inflammatory cell infiltration, fibroblast accumulation, Ashcroft fibrosis scores, and hydroxyproline deposition. Furthermore, IGF2BP1 knockdown downregulated PF-associated markers in lung tissues and embryonic lung fibroblasts (ELFs), including TGF-β1, α-SMA, Collagen-I/III, Arg1, CCL18, Ym1, CD163, IL-6, IL-1β, and TIMP1, while decreasing the CD68+/CD163+ macrophage proportion. Mechanistic studies revealed that IGF2BP1 bound to and stabilized thrombospondin-1 (THBS1) in an m6A-dependent manner. THBS1 overexpression rescued the suppression of macrophage M2 polarization caused by IGF2BP1 knockdown. Additionally, THBS1 overexpression counteracted IGF2BP1 knockdown-mediated inhibition of glycolysis, restoring HK2, LDHA, and PKM2 expression, lactate/glucose metabolism, and ATP production. Intriguingly, THBS1 physically interacted with toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), and TLR4 overexpression reversed the inhibitory effect of THBS1 knockdown on macrophage M2 polarization and glycolytic reprogramming. Collectively, our findings demonstrate that IGF2BP1 drives PF progression by stabilizing THBS1 mRNA via m6A modification, thereby promoting TLR4-mediated macrophage M2 polarization and glycolytic activation. This study unveils a novel IGF2BP1/THBS1/TLR4 regulatory axis in PF pathogenesis, offering potential therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Glycolytic metabolism; Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 1; Macrophage polarization; Pulmonary fibrosis; Thrombospondin-1; n6-methyladenosine.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval: Animal ethical approval for the present study was obtained from the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, China (Approval number: 202400044). Consent to participate: N/A. Consent for publish: N/A. Competing interests: All authors declare no conflicts of interest associated with this manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Iguratimod improves bleomycin-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis by regulating macrophage polarization through inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB pathway.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 13;16:1558903. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1558903. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40181990 Free PMC article.
-
FOXM1-activated IGF2BP3 promotes cell malignant phenotypes and M2 macrophage polarization in hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting ferroptosis via stabilizing RRM2 mRNA in an m6A-dependent manner.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 May;480(5):3051-3066. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05170-2. Epub 2024 Dec 4. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39630361
-
Icariside Ⅱ attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by modulating macrophage polarization.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Dec 5;317:116810. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116810. Epub 2023 Jun 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37331450
-
METTL3-mediated m6A RNA methylation induces the differentiation of lung resident mesenchymal stem cells into myofibroblasts via the miR-21/PTEN pathway.Respir Res. 2023 Nov 28;24(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02606-z. Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 38017523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of m6A modification during macrophage metabolic reprogramming in human diseases and animal models.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 18;16:1521196. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1521196. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40066451 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Meyer KC (2017) Pulmonary fibrosis, part I: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and diagnosis. Expert Rev Respir Med 11:343–359. 10.1080/17476348.2017.1312346 - PubMed
-
- León-Román F, Valenzuela C, Molina-Molina M (2022) Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Med Clin (Barc) 159:189–194. 10.1016/j.medcli.2022.02.020 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

