Impairment of platelet mitochondrial respiration in patients with chronic kidney disease with and without diabetes
- PMID: 40220191
- PMCID: PMC12316832
- DOI: 10.1007/s11010-025-05280-5
Impairment of platelet mitochondrial respiration in patients with chronic kidney disease with and without diabetes
Abstract
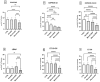
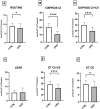
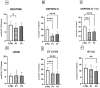
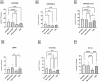
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) and diabetic kidney disease (DKD) are major public health problems, and their burden is growing relentlessly with the aging of the global population. Their early recognition is now a public health priority, and there is an unmet need for the identification of specific biomarkers in minimally invasive or non-invasive samples. Mitochondrial dysfunction plays a pivotal role in the development and progression of both CKD and DKD and circulating platelets have emerged as an ideal candidate for the assessment of the respiratory function. The present study assessed mitochondrial respiration in platelets isolated from the peripheral blood of patients with DKD and CKD compared to healthy controls. The study included a total number of 89 subjects, as follows: 30 DKD patients divided into three subgroups based on the urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (uACR): 20 normoalbuminuric, 10 microalbuminuric, and 10 macroalbuminuric, 29 CKD patients (positive controls) and 20 healthy individuals (negative controls). Platelets were isolated by differential centrifugations and a high-resolution respirometry protocol was adapted to assess mitochondrial respiration dependent on complex I (CI) and complex II (CII). A significant reduction of the CI-supported active respiration was found in the normoalbuminuric DKD patients and further decreased in the microalbuminuric DKD subgroup. Both CI and CII-dependent coupled respiration and the maximal uncoupled respiration were significantly reduced in the macroalbuminuric DKD subgroup. In conclusion, mitochondrial respiration impairment in peripheral platelets is evident from the early stages of DKD. Moreover, platelet mitochondrial respiration was more severely impaired in patients with macroalbuminuric DKD as compared to those with CKD. Further, more extensive follow-up studies are warranted to determine whether platelet respiratory mitochondrial dysfunction could serve as a peripheral biomarker for kidney mitochondrial dysfunction and/or as a prognostic tool in DKD.
Keywords: Albuminuria; Chronic kidney disease; Diabetic kidney disease; Platelet mitochondrial respiration.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: Danina M. Muntean is an Associate Editor at Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. Oana M. Aburel and Adrian Sturza are members of the Editorial Board of the same journal. Apart from the above-mentioned statements, the other authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. Ethical approval: The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee for Scientific Research of the “Victor Babeș” University of Medicine and Pharmacy from Timișoara (Nr. 54/09.11.2020) and the Ethics Committee of the “Pius Brînzeu” Timiș County Emergency Hospital (Nr. 222/04.02.2021).
Figures
References
-
- Stevens PE, Ahmed SB, Carrero JJ, Foster B, Francis A, Hall RK, Herrington WG, Hill G, Inker LA, Kazancıoğlu R, Lamb E, Lin P, Madero M, McIntyre N, Morrow K, Roberts G, Sabanayagam D, Schaeffner E, Shlipak M, Shroff R, Tangri N, Thanachayanont T, Ulasi I, Wong G, Yang C-W, Zhang L, Levin A (2024) KDIGO 2024 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 105:S117–S314. 10.1016/j.kint.2023.10.018 - PubMed
-
- Bello AK, Okpechi IG, Levin A, Ye F, Damster S, Arruebo S, Donner JA, Caskey FJ, Cho Y, Davids MR, Davison SN, Htay H, Jha V, Lalji R, Malik C, Nangaku M, See E, Sozio SM, Tonelli M, Wainstein M, Yeung EK, Johnson DW (2024) An update on the global disparities in kidney disease burden and care across world countries and regions. Lancet Glob Health 12:e382–e395. 10.1016/s2214-109x(23)00570-3 - PubMed
-
- Ndumele CE, Neeland IJ, Tuttle KR, Chow SL, Mathew RO, Khan SS, Coresh J, Baker-Smith CM, Carnethon MR, Després J-P, Ho JE, Joseph JJ, Kernan WN, Khera A, Kosiborod MN, Lekavich CL, Lewis EF, Lo KB, Ozkan B, Palaniappan LP, Patel SS, Pencina MJ, Powell-Wiley TM, Sperling LS, Virani SS, Wright JT, Rajgopal Singh R, Elkind MSV, Rangaswami J, Association obotAH (2023) A synopsis of the evidence for the science and clinical management of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome: a scientific statement from the American heart association. Circulation 148:1636–1664. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001186 - PubMed
-
- Pavkov ME, Collins AJ, Coresh J, Nelson RG (2018) Kidney disease in diabetes. In: Cowie CC, Casagrande SS, Menke A, Cissell MA, Eberhardt MS, Meigs JB, Gregg EW, Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Becker DJ, Brancati FL, Boyko EJ, Herman WH, Howard BV, Narayan KMV, Rewers M, Fradkin JE (eds) Diabetes in America. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (US), Bethesda - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

