Multiscale transformers and multi-attention mechanism networks for pathological nuclei segmentation
- PMID: 40221423
- PMCID: PMC11993704
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-90397-2
Multiscale transformers and multi-attention mechanism networks for pathological nuclei segmentation
Abstract
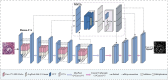
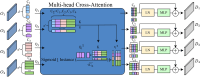
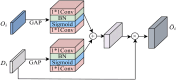
Pathology nuclei segmentation is crucial of computer-aided diagnosis in pathology. However, due to the high density, complex backgrounds, and blurred cell boundaries, it makes pathology cell segmentation still a challenging problem. In this paper, we propose a network model for pathology image segmentation based on a multi-scale Transformer multi-attention mechanism. To solve the problem that the high density of cell nuclei and the complexity of the background make it difficult to extract features, a dense attention module is embedded in the encoder, which improves the learning of the target cell information to minimize target information loss; Additionally, to solve the problem of poor segmentation accuracy due to the blurred cell boundaries, the Multi-scale Transformer Attention module is embedded between encoder and decoder, improving the transfer of the boundary feature information and makes the segmented cell boundaries more accurate. Experimental results on MoNuSeg, GlaS and CoNSeP datasets demonstrate the network's superior accuracy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Irshad, H., Veillard, A., Roux, L. & Racoceanu, D. Methods for nuclei detection, segmentation, and classification in digital histopathology: A review-current status and future potential. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng.7, 97–114 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Liu, S. et al. A generative adversarial network based on deep supervision for anatomical and functional image fusion. Biomed. Signal Process. Control100, 107011 (2025).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

