Microbiologically influenced corrosion in uncoated and coated Mild Steel
- PMID: 40221427
- PMCID: PMC11993770
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-90003-5
Microbiologically influenced corrosion in uncoated and coated Mild Steel
Abstract
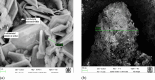
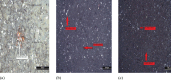
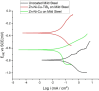
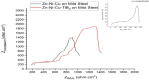
The study aimed to investigate the corrosion performance of Zn-Ni-Cu and Zn-Ni-Cu-TiB2 coatings in the microbial-induced environment (E-Coli, ATCC 25922, and 3.5%NaCl solution). Zn-Ni-Cu and Zn-Ni-Cu-TiB2 were surfaces coated on an ASTM A-36 Steel substrate utilizing a high-velocity oxy-fuel (HVOF) thermal spray process. Immersion tests following ASTM G-31, and ASTM G1-03, standards were performed in Escherichia Coli (E-Coli, American Type Culture CollectionATCC25922) bacteria medium. The effect of Zn, Ni, and Ti was studied in preventing microbial-induced corrosion.SEM, and XRD analysis before and after helped to understand the morphological and structural changes in coated/uncoated ASTM A-36 steel. Various forms of rust were ascertained in XRD analysis. The inclusion of Zn and Cu inhibited bacterial attachment to the coated surface, hence preventing significant corrosion of the underlying substrate. The coatings performed effectively and inhibited bacterial growth. The uncoated ASTM A-36 Steel specimen showed well-developed bacterial colonies on the surface and in the solution medium. All forms of rust were reported in XRD analysis for uncoated ASTM A-36 steel while few forms of rust were reported in coated ASTM A-36 steel.Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and Tafel polarization in Escherichia coli (E-Coli, ATCC 25922) medium demonstrated that the coated samples had greater corrosion resistance than the uncoated ASTM A-36 Steel specimens. The higher corrosion potential (Ecorr) values of the two coated samples indicated improved anodic protection.
Keywords: Airborne reactive oxygen species; Bacterium Escherichia Coli; Biotic environment; High-velocity oxy-fuel spraying; Microbiologically- Induced Corrosion.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: No plagiarism was incorporated in this research. The literature is cited appropriately. Consent to participate: The corresponding author and co-author agree to participate in any review or discussion process. Consent for publication: The corresponding author and co-author agree to publish this manuscript in your prestigious journal.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Microstructure, corrosion and tribological and antibacterial properties of Ti-Cu coated stainless steel.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2015 Oct;50:23-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2015.06.004. Epub 2015 Jun 10. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2015. PMID: 26093948
-
Production and characterization of low-density silicon nitride reinforced zinc nanocomposite coatings on mild steel for applications in marine and automotive industries.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 10;10(16):e36000. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36000. eCollection 2024 Aug 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39253202 Free PMC article.
-
Corrosion resistance and antibacterial activity of zinc-loaded montmorillonite coatings on biodegradable magnesium alloy AZ31.Acta Biomater. 2019 Oct 15;98:196-214. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.05.069. Epub 2019 May 31. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 31154057
-
Microbial Corrosion Resistance and Antibacterial Property of Electrodeposited Zn-Ni-Chitosan Coatings.Molecules. 2019 May 22;24(10):1974. doi: 10.3390/molecules24101974. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31121968 Free PMC article.
-
An investigation of the corrosion behavior of zinc-coated stainless steel orthodontic wires: the effect of physical vapor deposition method.BMC Oral Health. 2024 May 9;24(1):501. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04242-5. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38725023 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashton, S. A., Miller, J. D. A. & King, R. A. Corrosion of Ferrous metals in batch cultures of Nitrate-Reducingu Bacteria. Br. Corros. J.8 (4), 185–189 (1973).
-
- Aleaghil, S. A. et al. Antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles on Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Adv. Biotechnol. Res.7 (3), 1569–1575 (2016).
-
- Ali, S. I. & Ahmad, S. N. Corrosion behaviour OF HVOF deposited Zn–Ni–Cu and Zn–Ni–Cu–TiB2 coatings on mild steel. Corros. Rev.10.1515/corrrev-2021-0082 (2022).
-
- Ali, S. I. & Ahmad, S. N. Erosion behavior of Zn-Ni-Cu and Zn-Ni-Cu-TiB2 coated mild steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform.32, 1–12. (2022).
-
- Ali, S. I. & Ahmad, S. N. Tribo-corrosion behavior of Zn-Ni-Cu and Zn-Ni-Cu-TiB2 coated mild steel. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 16(5), 104648. (2023).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

