Local patterns of genetic sharing between neuropsychiatric and insulin resistance-related conditions
- PMID: 40221434
- PMCID: PMC11993748
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-025-03349-9
Local patterns of genetic sharing between neuropsychiatric and insulin resistance-related conditions
Abstract
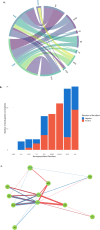
The co-occurrence of insulin resistance (IR)-related metabolic conditions with neuropsychiatric disorders is a major public health challenge. Evidence of the genetic links between these phenotypes is emerging, but little is currently known about the genomic regions and biological functions that are involved. To address this, we performed Local Analysis of [co]Variant Association (LAVA) using large-scale (N = 9,725-933,970) genome-wide association studies (GWASs) results for three IR-related conditions (type 2 diabetes mellitus, obesity, and metabolic syndrome) and nine neuropsychiatric disorders. Subsequently, positional and expression quantitative trait locus (eQTL)-based gene mapping and downstream functional genomic analyses were performed on the significant loci. Patterns of negative and positive local genetic correlations (|rg| = 0.21-1, pFDR < 0.05) were identified at 109 unique genomic regions across all phenotype pairs. Local correlations emerged even in the absence of global genetic correlations between IR-related conditions and Alzheimer's disease, bipolar disorder, and Tourette's syndrome. Genes mapped to the correlated regions showed enrichment in biological pathways integral to immune-inflammatory function, vesicle trafficking, insulin signalling, oxygen transport, and lipid metabolism. Colocalisation analyses further prioritised 10 genetically correlated regions for likely harbouring shared causal variants, displaying high deleterious or regulatory potential. These variants were found within or in close proximity to genes, such as SLC39A8 and HLA-DRB1, that can be targeted by supplements and already known drugs, including omega-3/6 fatty acids, immunomodulatory, antihypertensive, and cholesterol-lowering drugs. Overall, our findings highlight the complex genetic architecture of IR-neuropsychiatric multimorbidity, advocating for an integrated disease model and offering novel insights for research and treatment strategies in this domain.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: AS is or has been a consultant/speaker for Abbott, Abbvie, Angelini, AstraZeneca, Clinical Data, Boehringer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Innovapharma, Italfarmaco, Janssen, Lundbeck, Naurex, Pfizer, Polifarma, Sanofi, Servier, and Taliaz. BF discloses having received educational speaking fees and travel support from Medice. CF was a speaker for Janssen. GP is director/chief scientific officer and WDW as well as IHR are employees of Drug Target ID, Ltd., but their activities at this company do not constitute competing interests with regard to this paper. JH has received lecture honoraria as part of continuing medical education programs sponsored by Shire, Takeda, Medice, and Biocodex. JSS reported receiving research support through his institution from the Patrimonio Comunal Olivarero, Almond Board of California and Pistachio Growers of California; he is serving on the board of and receiving grant support through his institution from the International Nut and Dried Foundation, Instituto Danone Spain and Institute Danone International. FFA and SJM have been consultants/speakers for NovoNordisk. All other authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Ethics: We used publicly available summary statistics of genome-wide association studies (GWASs) conducted by external authors and consortia; thus, no specific authorisation was required from the local Ethics Committee. No individual genotypic data were used or collected.
Figures
Update of
-
Local patterns of genetic sharing challenge the boundaries between neuropsychiatric and insulin resistance-related conditions.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 8:2024.03.07.24303921. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.07.24303921. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Transl Psychiatry. 2025 Apr 12;15(1):145. doi: 10.1038/s41398-025-03349-9. PMID: 38496672 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Possidente C, Fanelli G, Serretti A, Fabbri C. Clinical insights into the cross-link between mood disorders and type 2 diabetes: a review of longitudinal studies and Mendelian randomisation analyses. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2023;152:105298. - PubMed
-
- Fanelli G, Serretti A. Depression, antidepressants, and insulin resistance: which link? Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022;60:4–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

