Interplay between MRI radiomics and immune gene expression signatures in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 40221527
- PMCID: PMC11993570
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-96821-x
Interplay between MRI radiomics and immune gene expression signatures in oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
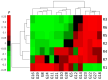
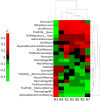
With the advances in immunotherapy and the challenge of poor responsiveness in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) patients, understanding the tumor microenvironment is crucial. Radiogenomics offers the potential to provide pre-operative, non-invasive image-derived immune biomarkers. To this aim, the present study explores the capability of MRI-based radiomics to describe patients' immune state in OSCC. Seven MRI-based radiomic, 29 immune-related gene expression signatures were computed and deconvolution analysis was performed for a subset of OSCC from the BD2Decide database. A correlation-driven analysis identified key associations between radiomic and immune-related signatures and cell populations. Radiomic classifiers of the gene expression signatures were then developed to evaluate their capability to stratify patients based on immune status. MRI-based radiomic models showed promising results in predicting a gene expression signature associated with significant prognostic value for HNSCC patients who underwent radiotherapy (AUC = 0.92), suggesting these models' potential in distinguishing radioresistant from radiosensitive patients, aiding treatment decisions. Additionally, radiomic signatures reflected immune infiltrating cells in our cohort (M1, CD8 + T, B cells). MRI-radiomic signatures and associated models could become non-invasive methods to evaluate the prognosis and treatment choice in OSCC patients. Based on our promising results, and upon external validation, MRI-radiomics could enhance personalized medicine approaches.
Keywords: Cluster analysis; Head and neck cancer; Magnetic resonance imaging; Radiogenomic; Radiomic features; Transcriptomic signatures; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The protocols were approved by the Ethical Committees of the participating centers, and data acquisition followed the General Data Protection Regulation of the EU. All patients signed the informed consent. Consent for publication: All authors have read and approved the manuscript and agree with submission.
Figures




References
-
- Bray, F. et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin.74, 229–263 (2024). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

