Morpho-phytochemical screening and biological assessments of aerial parts of Iranian populations of wild carrot (Daucus carota L. subsp. carota)
- PMID: 40221589
- PMCID: PMC11993562
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-96965-w
Morpho-phytochemical screening and biological assessments of aerial parts of Iranian populations of wild carrot (Daucus carota L. subsp. carota)
Abstract
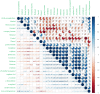
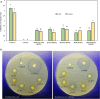
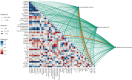
This study investigated the morphological and phytochemical characteristics of 118 genotypes of Daucus carota L. subsp. carota, collected from natural habitats in five populations across West Azerbaijan. The main objectives were to evaluate the variability among these populations and to explore their correlations with the local climatic conditions. The ultimate goal was to identify potential candidates for domestication and contribute to pre-breeding programs. Our findings revealed notable differences in plant height (PH), which ranged from 71.96 cm to 96.08 cm, with the tallest samples originating from the Gharib Hassan population (DCP5). The number of nodes on the main branch (NNMMB) was highest in DCP3 and DCP5, with mean values of 6.44 and 6.13, respectively. Essential oil (EO) content varied among the populations, from 0.88 to 1.37 (% V/W), peaking in DCP3. Gas chromatography (GC) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analyses detected 23 chemical compounds, accounting for 88.49% to 95.5% of the essential oils. The primary compounds included oxygenated sesquiterpenes (47.84% to 76.26%) and hydrocarbon monoterpenes (2.33% to 37.37%). Carotol was the dominant compound in all populations, particularly high in DCP4 (74.03%) and DCP5 (73.61%). Based on essential oil composition, populations were classified into distinct chemotypes: DCP1 as chemotype I (carotol-bornyl acetate), DCP3 as chemotype II (carotol-α-pinene), and DCP2, DCP4, and DCP5 as chemotype III (carotol content of 64.03% to 74.03%). Correlation analysis revealed a significant negative relationship between carotol and several compounds, including daucene (-0.83), β-pinene (-0.65). Among the aerial parts, DCP3 had the highest total phenolic content (54.81 mg GAE/g DW), while DCP2 and DCP3 exhibited high total flavonoid content in seeds (36.07 and 36.22 mg QE/g DW), respectively. Antibacterial activity tests showed that DCP3 and DCP5 had notable inhibitory effects against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Using circular cluster analysis, the genotypes were categorized into three main groups based on the assessed traits, revealing greater variability in phytochemical and morphological characteristics among different populations compared to variations within individuals.
Keywords: Antibacterial activity; Canonical correspondence analysis; Carotol, Heretical cluster analysis; DPPH%; Essential oil; Stepwise regression; Total flavonoid contents; Total phenolic contents.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical statement: Plant sampling were comply with the IUCN Policy Statement on Research Involving Species at Risk of Extinction and the Convention on the Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Essential oil composition, morphological characterization, phenolic content and antioxidant activity of Iranian populations of Hymenocrater longiflorus Benth. (Lamiaceae).Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 27;14(1):7239. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57826-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38538705 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Activity and Chemical Characterization of Daucus carota subsp. maximus Essential Oils.Chem Biodivers. 2017 May;14(5). doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201600477. Epub 2017 Apr 17. Chem Biodivers. 2017. PMID: 28171692
-
Essential oils of Daucus carota subsp. carota of Tunisia obtained by supercritical carbon dioxide extraction.Nat Prod Commun. 2010 Dec;5(12):1955-8. Nat Prod Commun. 2010. PMID: 21299130
-
Chemical composition and biological activities of essential oils of seven Cultivated Apiaceae species.Sci Rep. 2024 May 2;14(1):10052. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60810-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38698117 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Composition, Functional and Anticancer Properties of Carrot.Molecules. 2023 Oct 19;28(20):7161. doi: 10.3390/molecules28207161. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37894640 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rabizadeh, F., Amini, E. & Nasrollahi, F. The anatomical and micromorphological properties of endemic species to gypsic soils of Semnan. Iran. J. Struct. Biol.215, 107968 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Manafzadeh, S., Staedler, Y. M. & Conti, E. Visions of the past and dreams of the future in the Orient: the Irano-Turanian region from classical botany to evolutionary studies. Biol. Rev.92, 1365–1388 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Sousa, R. M. O., Cunha, A. C. & Fernandes-Ferreira, M. The potential of Apiaceae species as sources of singular phytochemicals and plant-based pesticides. Phytochemistry187, 112714 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Hussain, A. I. Characterization and biological activities of essential oils of some species of Lamiaceae (University of Agriculture, 2009).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

