Can vildagliptin protect against radiation-induced premature ovarian failure? Insights into the AMPK and AKT signaling pathways
- PMID: 40221811
- PMCID: PMC11994011
- DOI: 10.1186/s40360-025-00903-5
Can vildagliptin protect against radiation-induced premature ovarian failure? Insights into the AMPK and AKT signaling pathways
Abstract
Background: Among the detrimental side effects caused by radiotherapy in young females is the ovarian damage, eventually causing premature ovarian failure (POF). While many signaling pathways contribute to the pathogenesis of POF, to date no sufficient data exist on the AMPK and AKT signaling pathways in irradiated ovaries. Both AMPK and AKT play crucial roles in the process of folliculogenesis. Vildagliptin (vilda) is a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor with modulatory effect on both AMPK and AKT. Therefore, our study aimed to investigate the biochemical changes that occur in the AMPK/AKT signaling pathway, and the effect of co-administration of vildagliptin in radiation-induced POF.
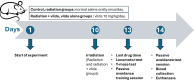
Methods: Female Sprague-dawley rats were randomly divided into four groups: control, radiation, radiation + vilda, or vilda alone groups. Vilda was administered orally once/day, and on the 10th day of the experiment, radiation and radiation + vilda group rats were subjected to 3.2 Gy of whole-body gamma irradiation. Behavioral activity was assessed on the 13th day of the experiment. On day 14 of the experiment, all rats were euthanized. Serum samples were collected, and ovaries were dissected for histological and biochemical analyses.
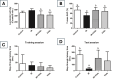
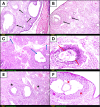
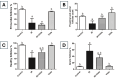
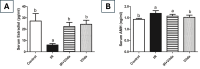
Results: Irradiation of female rats resulted in increased locomotor hyperactivity, impaired memory, and ovarian damage as evidenced by the marked histopathological deterioration. Additionally, irradiation led to a significant decrease in body weight gain, gonadosomatic index, and serum estradiol level. Further, it caused a significant increase in serum AMH, phosphorylated AMPK, phosphorylated AKT, cytoplasmic Nrf2 expression and phosphorylated CREB levels. Co-administration of vilda exhibited neuroprotective effects, preserved the ovarian histological architecture but failed to preserve the primordial follicle pool in irradiated rats.
Conclusion: In conclusion, AMPK/AKT signaling pathway is upregulated in radiation-induced POF. It possibly contributes to POF pathogenesis by accelerating the activation of primordial follicles, hence leading to their premature depletion. Coadministration of vilda can protect the ovaries and temporarily preserve its endocrine function; however, it does not sustain the ovarian reproductive capacity due to the early depletion of the pool of primordial follicles. Women undergoing radiotherapy should be cautious with the use of AKT-activating drugs.
Keywords: AKT; AMPK; CREB; Ionizing radiation; Ovaries; Vildagliptin.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval: The study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Pharmacy, Ain Shams University, Egypt (Approval number: 88). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

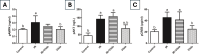
Similar articles
-
Potential mitigating impact of a dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor, vildagliptin, on oxazolone-induced ulcerative colitis: Targeting the role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR and AMPK/Nrf2 signaling pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 May 30;133:112110. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112110. Epub 2024 Apr 22. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38652960
-
Vildagliptin attenuates acetic acid-induced colitis in rats via targeting PI3K/Akt/NFκB, Nrf2 and CREB signaling pathways and the expression of lncRNA IFNG-AS1 and miR-146a.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Mar;92:107354. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107354. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33434756
-
Vildagliptin restores cognitive function and mitigates hippocampal neuronal apoptosis in cisplatin-induced chemo-brain: Imperative roles of AMPK/Akt/CREB/ BDNF signaling cascades.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Mar;159:114238. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114238. Epub 2023 Jan 12. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36640673
-
Hesperidin attenuates radiation-induced ovarian failure in rats: Emphasis on TLR-4/NF-ĸB signaling pathway.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2024 Nov;492:117111. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2024.117111. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39326792
-
Targeting autophagy in premature ovarian failure: Therapeutic strategies from molecular pathways to clinical applications.Life Sci. 2025 Apr 1;366-367:123473. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2025.123473. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39971127 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

