Comprehensive analysis of UPK3B as a marker for prognosis and immunity in pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 40223017
- PMCID: PMC11994762
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-97213-x
Comprehensive analysis of UPK3B as a marker for prognosis and immunity in pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Abstract
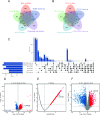
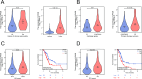
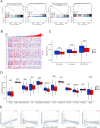
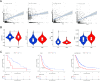
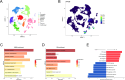
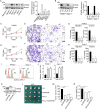
The low immunogenicity of pancreatic cancer inhibits effective antitumor immune responses, primarily due to the immune evasion mediated by low expression of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC). Through comprehensive analysis, our study identifies UPK3B as a gene closely associated with low MHC expression and low immunogenicity in pancreatic cancer. UPK3B has been reported as a marker of primary mesothelial cells, mature epicardium and promotes extracellular matrix signaling. However, the role of UPK3B in pancreatic cancer remain unclear. We found that UPK3B is highly predictive of overall survival (OS) in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and is significantly related to clinical features, immune cell infiltration, and response to immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy. Gene enrichment analysis revealed significant downregulation of immune regulatory and BCR signaling pathways in the UPK3B high-expression group. Additionally, UPK3B is positively correlated with immunosuppressive cells, suggesting that high UPK3B expression may inhibit antitumor immune responses by promoting low MHC expression. UPK3B is also positively correlated with immune checkpoints, indicating that tumors with high UPK3B expression may not benefit from ICI therapy. Therefore, UPK3B may serve as a novel biomarker and therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: Biomarker; Immunosuppression; MHC; Pancreatic Cancer; Prognosis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82203330 , 82002590/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82203330 , 82002590/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022M711589/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- YKK22065/Nanjing Health Science and Technology Development Project
- YKK22267/Nanjing Health Science and Technology Development Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

