Correction: Combination of betulinic acid and EGFR‑TKIs exerts synergistic anti‑tumor effects against wild‑type EGFR NSCLC by inducing autophagy‑related cell death via EGFR signaling
- PMID: 40223044
- PMCID: PMC11995596
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-025-03223-8
Correction: Combination of betulinic acid and EGFR‑TKIs exerts synergistic anti‑tumor effects against wild‑type EGFR NSCLC by inducing autophagy‑related cell death via EGFR signaling
Figures

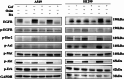
Erratum for
-
Combination of betulinic acid and EGFR-TKIs exerts synergistic anti-tumor effects against wild-type EGFR NSCLC by inducing autophagy-related cell death via EGFR signaling pathway.Respir Res. 2024 May 20;25(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02844-9. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 38764025 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

