The Differential Association Between Leadership Styles and Organizational Silence in a Sample of Chinese Nurses: A Multi-Indicator and Multicause Study
- PMID: 40223875
- PMCID: PMC11985246
- DOI: 10.1155/jonm/9626175
The Differential Association Between Leadership Styles and Organizational Silence in a Sample of Chinese Nurses: A Multi-Indicator and Multicause Study
Abstract
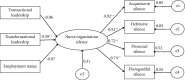
Objective: To determine the effect of diverse leadership styles on the organizational silence of nurses and the association between demographic factors and organizational silence of nurses. Background: Organizational silence prevails among nurses, threatening patient safety and hospital innovation. Transformational and transactional leadership negatively affect nurses' organizational silence, but further confirmation is needed. Methods: The 545 clinical nurses from four hospitals in Shenzhen completed the online self-report questionnaires including multivariate leadership style scale and nurses' organizational silence assessment questionnaire.The data were analyzed by SPSS26.0 software using analysis of variance and Pearson's correlation. The Multiple Indicators Multiple Causes (MICIC) model was used to analyze the influencing factors of organizational silence using AMOS 24. Results: The results of the univariate analysis revealed that the differences in the organizational silence scores of the nurses based on demographic factors such as age, gender, professional title, and undertaking nursing management tasks were not significant (all p > 0.05). However, the difference in the employment status was significant (p < 0.05). The MICIC model showed that the transformational leadership can aggravate this organizational silence of the nurses (β = 0.59, p < 0.001), whereas transactional leadership style and employment status had no significant effects (both p > 0.05). Conclusion: The organizational silence of nurses was at a moderately low level and transformational leadership style contributes to organizational silence of the nurses. The findings of this study suggested that nursing managers should strive for authentic and open leadership, pay attention to individual differences, and adjust their leadership style according to the preferences and needs of nurses, achieving personalized adaptation of leadership.
Keywords: Chinese nurse; differential association; leadership style; multiple indicators; organizational silence.
Copyright © 2025 Guangling Hu et al. Journal of Nursing Management published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wu W., Zhang J., Zhang Y., Chen C. Qualitative Study on Organizational Silence Behavior Experience of Junior Nurses. Hospital Management Forum . 2023;40(9):57–59.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources