NKCC1 inhibition improves sleep quality and EEG information content in a Down syndrome mouse model
- PMID: 40224007
- PMCID: PMC11986984
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112220
NKCC1 inhibition improves sleep quality and EEG information content in a Down syndrome mouse model
Abstract
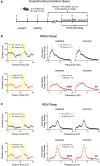
In several brain disorders, the hyperpolarizing/inhibitory effects of GABA signaling through Cl-permeable GABAA receptors are compromised, leading to an imbalance between neuronal excitation and inhibition. For example, the Ts65Dn mouse model of Down syndrome (DS) exhibits increased expression of the Cl- importer NKCC1, leading to depolarizing gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) signaling in the mature hippocampus and cortex. Inhibiting NKCC1 with the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved diuretic bumetanide rescues inhibitory GABAergic transmission, synaptic plasticity, and cognitive functions in adult Ts65Dn mice. Given that DS individuals and Ts65Dn mice show sleep disturbances, and considering the key role of GABAergic transmission in sleep, we investigated whether NKCC1 upregulation contributes to sleep abnormalities in adult Ts65Dn mice. Chronic oral administration of bumetanide ameliorated the spectral profile of sleep, sleep architecture, and electroencephalogram (EEG) entropy/complexity, accompanied by a lower hyperactivity in trisomic mice. These results offer a potential avenue for addressing common sleep disturbances in DS.
Keywords: Molecular biology; Neuroscience.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
L.C. is named as co-inventor on granted patent US 9822368, EP 3083959, JP 6490077; IT 102019000004929; and US11427836. L.C. is also named as co-inventor on the patent applications WO 2018/189225 and PA102109IT101. L.C. is founder and scientific advisor at IAMA therapeutics S.r.l.
Figures


References
-
- Dierssen M. Down syndrome: The brain in trisomic mode. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012;13:844–858. - PubMed
-
- Stores R.J. Sleep problems in adults with Down syndrome and their family carers. J. Appl. Res. Intellect. Disabil. 2019;32:831–840. - PubMed
-
- Maris M., Verhulst S., Wojciechowski M., Van de Heyning P., Boudewyns A. Outcome of adenotonsillectomy in children with Down syndrome and obstructive sleep apnoea. Arch. Dis. Child. 2017;102:331–336. - PubMed
-
- Grubar J.C., Gigli G.L., Colognola R.M., Ferri R., Musumeci S.A., Bergonzi P. Sleep patterns of Down’s syndrome children: Effects of butoctamide hydrogen succinate (BAHS) administration. Psychopharmacology. 1986;90:119–122. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

