Effect of Vietnamese coriander Powder on Growth, Body Composition, Hematology, and Immune-Related Gene Expression in Nile Tilapia
- PMID: 40224247
- PMCID: PMC11986921
- DOI: 10.1155/vmi/1253764
Effect of Vietnamese coriander Powder on Growth, Body Composition, Hematology, and Immune-Related Gene Expression in Nile Tilapia
Abstract
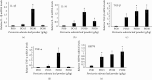
Dietary supplementation of plant herbs into aquafeed is recommended for intensive and sustainable aquaculture practices. This study has investigated the effect of Persicaria odorata (PO) leaf powder on growth, feed utilization, whole-body composition, hematology, and immune-related gene expression in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish (∼7.77 ± 0.01 g/fish) were randomly allocated into four treatment groups, each with three replicates. They were fed with dietary supplementation of PO at concentrations of 0, 15, 30, and 50 g/kg (termed PO0-PO50) for 10 weeks. Results indicated that the final body weight, weight gain, and specific growth rate were significantly higher at all PO supplementation levels compared to the control, with the highest value in the PO30 group. Similarly, the protein efficiency ratio and protein productive value in all PO groups were significantly higher than those of the control group. Red blood cells, white blood cells, and hemoglobin levels showed quadratic increases in the PO groups. In addition, total protein, globulin, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol were linearly and quadratically increased with increasing PO levels, but alanine aminotransferase activity was linearly and quadratically decreased. Furthermore, dietary PO supplementation linearly decreased triglyceride and lipoprotein cholesterol levels, with the lowest levels found in the PO15 group. The expression of genes related to immunity showed that dietary supplementation of PO significantly increased the expression of proinflammatory factors (IL-1β and TNF-α), anti-inflammatory (IL-10 and TGF-β), and HSP70. In addition, glucose and cortisol levels decreased in all PO-supplemented groups, with the lowest levels found in the PO50 and PO30 groups, respectively. These findings showed that a dietary intervention with PO could improve growth, feed utilization, hematological parameters, upregulating genes related to immunity, and decreasing stress markers in Nile tilapia. Consequently, the utilization of PO at a dosage of 30 g/kg could contribute to the sustainable development of the aquaculture sector.
Keywords: Nile tilapia; Persicaria odorata; growth performance; herb; immunity.
Copyright © 2025 Apisara Honghirun et al. Veterinary Medicine International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of dietary Hericium erinaceus extract on growth, nutrient utilization, hematology, expression of genes related immunity response, and disease resistance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus).Fish Physiol Biochem. 2024 Dec;50(6):2519-2534. doi: 10.1007/s10695-024-01399-2. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39240421
-
Synergistic Effects Between Dietary Zinc Form Supplementation and Dietary Protein Levels on Performance, Intestinal Functional Topography, Hemato-biochemical Indices, Immune, Oxidative Response, and Associated Gene Expression of Nile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022 Jul;200(7):3412-3428. doi: 10.1007/s12011-021-02911-y. Epub 2021 Sep 6. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022. PMID: 34487300
-
The effects of dietary yeast hydrolysate on growth, hematology, antioxidant enzyme activities and non-specific immunity of juvenile Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020 Jun;101:168-175. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2020.03.037. Epub 2020 Mar 21. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32209396
-
Effect of phytase enzyme on growth performance, serum biochemical alteration, immune response and gene expression in Nile tilapia.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018 Sep;80:97-108. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.05.051. Epub 2018 May 31. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29860070
-
A Blend of natural phytobiotics enhances growth performance, feed efficiency, and the immuno-health status of fingerlings of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus).Open Vet J. 2025 Feb;15(2):746-764. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2025.v15.i2.24. Epub 2025 Feb 28. Open Vet J. 2025. PMID: 40201808 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture Sustainability in Action . Rome, Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; 2020.
-
- Lulijwa R., Rupia E. J., Alfaro A. C. Antibiotic Use in Aquaculture, Policies and Regulation, Health and Environmental Risks: A Review of the Top 15 Major Producers. Reviews in Aquaculture . 2019;12(2):640–663. doi: 10.1111/raq.12344. - DOI
-
- Leung T. L., Bates A. E. More Rapid and Severe Disease Outbreaks for Aquaculture at the Tropics: Implications for Food Security. Journal of Applied Ecology . 2013;50(1):215–222. doi: 10.1111/1365-2644.12017. - DOI
-
- Vaseeharan B., Thaya R. Medicinal Plant Derivatives as Immunostimulants: An Alternative to Chemotherapeutics and Antibiotics in Aquaculture. Aquaculture International . 2014;22(3):1079–1091. doi: 10.1007/s10499-013-9729-3. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

