The effect of vagal nerve stimulation treatment on autonomic nervous system in patients with refractory epilepsy
- PMID: 40224309
- PMCID: PMC11985422
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1566497
The effect of vagal nerve stimulation treatment on autonomic nervous system in patients with refractory epilepsy
Abstract
Introduction: Vagal nerve stimulation (VNS) is a treatment that can be used in drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE) patients who are not suitable for resective surgery. Effects of VNS on the autonomic system are controversial. In our study, we examined SSR and R-R interval variability (RR-IV) to evaluate autonomic functions in patients with refractory epilepsy treated with and without VNS and healthy volunteers.
Methods: Our study included 41 healthy volunteers without any disease or drug administration, 38 DRE patients without VNS, and 38 DRE patients with VNS. Electrophysiological tests of sympathetic skin response (SSR) and RR interval variability (RR-IV) analysis were performed.
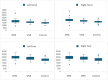
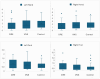
Results: While no statistically significant difference was observed between the SSR latencies and amplitudes of the DRE group with VNS and the DRE group without VNS, when the SSR latencies of the 4 extremities of the DRE groups with and without VNS and the control group were compared, it was observed that both groups had statistically significantly longer SSR latencies in all extremities compared to the control group. A statistically significant difference was observed between the DRE with VNS group and the control group and RR-IV was lower in the DRE with VNS group.
Conclusion: In conclusion, our study is one of the rare studies investigating the effects of VNS on the sympathetic system in patients with refractory epilepsy. According to the SSR and RR-IV results in our study, there was no evidence that VNS caused sympathetic dysfunction. However, VNS may cause a shift in cardiac sympathovagal balance toward sympathetic dominance.
Keywords: R-R interval variability; autonomic nervous system; drug-resistant epilepsy; sympathetic skin response; vagal nerve stimulation.
Copyright © 2025 Genç, Korucuk and Uçan Tokuç.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources