Skin and Wound Healing: Conventional Dosage versus Nanobased Emulsions Forms
- PMID: 40224422
- PMCID: PMC11983225
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c00455
Skin and Wound Healing: Conventional Dosage versus Nanobased Emulsions Forms
Abstract
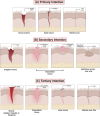
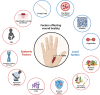
The skin plays a crucial role in the body's homeostasis through its thermoregulation functions, metabolic activity, and, mainly, its barrier function. Once this system has its homeostasis disturbed, through the promotion of tissue discontinuity, an injury happens and a restoration process starts. Different products can be used to promote, accelerate, or stimulate the healing process, such as hydrogels, emulsions, and ointments (main conventional formulations). Despite the historical use and wide market and consumer acceptance, new systems emerged for wound management with the main challenge to overcome conventional form limitations, in which nanosystems are found, mainly nanobased emulsion forms (nano- and microemulsions, NE and ME). Here, we discuss the skin function and wound healing process, highlighting the cellular and molecular processes, the different wound classifications, and factors that affect physiological healing. We also investigated the recent patents (2012-2023) filed at the United States Patent and Trademark Office, where we found few patents for conventional forms (hydrogels = 5; emulsions = 4; ointments = 6) but a larger number of patents for nanobased emulsions filed in this time (NE = 638; ME = 4,072). Furthermore, we address the use of nanobased emulsions (NE and ME) and their particularities, differences, and application in wound treatment. This work also discusses the challenges, bottlenecks, and regulatory framework for nanosystems, industrial, academic, and government interest in nanotechnology, and future perspectives about this key factor for the nanosystems market and consumer acceptance.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Piezoelectric hydrogels for accelerating healing of diverse wound types.Biomater Sci. 2025 Jan 28;13(3):568-586. doi: 10.1039/d4bm01347f. Biomater Sci. 2025. PMID: 39714223 Review.
-
Topical application of omega-3-, omega-6-, and omega-9-rich oil emulsions for cutaneous wound healing in rats.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2019 Apr;9(2):418-433. doi: 10.1007/s13346-018-0522-8. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 29667150
-
Nanotechnology and Protection of Intellectual Property: Emerging Trends.Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2020;14(4):307-327. doi: 10.2174/1872210514666200612174317. Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32532198
-
Lipid-based nanosystems for wound healing.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2024 Aug;21(8):1191-1211. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2024.2391473. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2024. PMID: 39172249 Review.
-
Preparation and in vivo evaluation of a topical hydrogel system incorporating highly skin-permeable growth factors, quercetin, and oxygen carriers for enhanced diabetic wound-healing therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Jul 18;14:5449-5475. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S213883. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31409998 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fortune Business Insights . Advanced Wound Care Market Size, Share & Industry Analysis, By Product Type (Advanced Wound Dressings {Alginate Dressings, Hydrogel Dressings, Film Dressings, Hydrocolloid Dressings, Antimicrobial Dressings, Foam Dressings, and Others}, Wound Care Devices {Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT), Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy), Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT), and Others}, and Active Wound Care), By Indication (Diabetic Foot Ulcers, Pressure Ulcers, and Others), By End User (Hospitals, Clinics and Others), and Regional Forecast, 2024-2032. https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/advanced-wound-....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
