dia-PASEF Proteomics of Tumor and Stroma LMD Enriched from Archived HNSCC Samples
- PMID: 40224439
- PMCID: PMC11983184
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c11051
dia-PASEF Proteomics of Tumor and Stroma LMD Enriched from Archived HNSCC Samples
Abstract
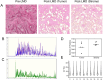
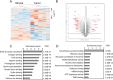
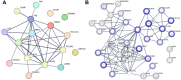
We employed laser microdissection to selectively harvest histology-resolved tumors and stroma from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) tissues. Peptide digests from the LMD-enriched HNSCC tissue were analyzed by quantitative mass-spectrometry-based proteomics using a data independent analysis approach. In paired samples, excellent proteome coverage was achieved, having quantified 6668 proteins with a median quantitative coefficient of variation under 10%. Significant differences in relevant functional pathways between the tumor and the stroma regions were observed. Extracellular matrix (ECM) was identified as a major component enriched in the stroma, including many cancer-associated fibroblast signature proteins in this compartment. We demonstrate the potential for comparative deep proteome analysis from a very low starting input in a scalable format. Correlating such results with clinical features or disease progression will likely enable the identification of novel targets for disease classification and interventions.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): AP, ALH, BVK, BD, JA, TPC, RG declare that they have no known competing financial interests. DA, MW are employees of Bruker Scientific.
Figures
Update of
-
dia-PASEF Proteomics of Tumor and Stroma LMD Enriched from Archived HNSCC Samples.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 10:2024.08.09.607341. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.09.607341. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: ACS Omega. 2025 Mar 25;10(13):13296-13302. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c11051. PMID: 39149249 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Patel V.; Hood B. L.; Molinolo A. A.; Lee N. H.; Conrads T. P.; Braisted J. C.; Krizman D. B.; Veenstra T. D.; Gutkind J. S. Proteomic Analysis of Laser-Captured Paraffin-Embedded Tissues: A Molecular Portrait of Head and Neck Cancer Progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14 (4), 1002–1014. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1497. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
