Insomnia Comorbid With Depression: A Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis of Research Trends and Hotspots From 2000 to 2024
- PMID: 40224524
- PMCID: PMC11991824
- DOI: 10.1155/bn/7106629
Insomnia Comorbid With Depression: A Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis of Research Trends and Hotspots From 2000 to 2024
Abstract
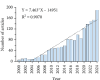
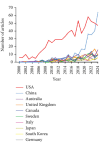
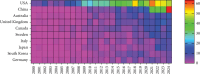
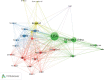
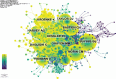
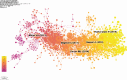
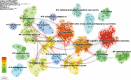
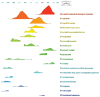
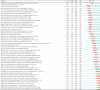
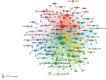
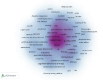
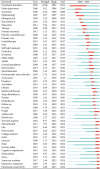
Background: Sleep disorders, such as insomnia, are pervasive and frequently comorbid with depression, significantly affecting the quality of life of patients. Insomnia is characterized by difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, which leads to impairment. Depression is characterized by persistent sadness and loss of interest, and it often features symptoms of insomnia. Understanding their interaction will be done for treatment strategies concerning both disorders. Despite the existence of extensive studies on insomnia and depression, there is a significant gap in bibliometric analysis specifically addressing the comorbidity of these two conditions. Objectives: This study is aimed at conducting a bibliometric analysis of research in insomnia comorbid with depression (ICD) to identify research trends, collaboration patterns, influential works, and hotspots. Methods: The study involved performance analysis to evaluate research productivity and trends, science mapping to visualize the intellectual structure and thematic evolution of the field, and network analysis to examine research collaboration and knowledge structure. Tools such as VOSviewer, CiteSpace, and GraphPad Prism were utilized for data analysis. Results: A total of 1624 publications on the comorbidity of insomnia and depression from 2000 to 2024 were included, encompassing both articles and reviews. Publication volume showed a steady growth from 2000 to 2008, followed by a significant increase from 2019 onward. The United States was the most productive country, followed by China. Key authors such as Allison G. Harvey, Charles M. Morin, and Daniel J. Buysse have made substantial contributions to the field. Major influential journals included Sleep Medicine, Journal of Affective Disorders, and Frontiers in Psychiatry. Research trends identified included the exploration of neurobiological mechanisms, cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-i), and personalized treatment approaches. Conclusion: This bibliometric analysis provides valuable insights into the evolving landscape of research on ICD. Future research should focus on personalized, multimodal interventions, expanding the application of CBT-i, exploring neurobiological mechanisms, and improving patients' quality of life through integrated treatment strategies.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis; comorbidity; depression; insomnia; visualization.
Copyright © 2025 Junting Chen et al. Behavioural Neurology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Drinčić T., van Dalfsen J. H., Kamphuis J., et al. The relationship between insomnia and the pathophysiology of major depressive disorder: an evaluation of a broad selection of serum and urine biomarkers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences . 2023;24(9):p. 8437. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098437. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

