Association of blood manganese levels with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in NHANES 2017-2020: A retrospective cross-sectional study
- PMID: 40224537
- PMCID: PMC11986999
- DOI: 10.1016/j.metop.2025.100358
Association of blood manganese levels with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in NHANES 2017-2020: A retrospective cross-sectional study
Abstract
Objective: This study investigates the link between blood manganese (Mn) levels and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in a U.S. adult population.
Background: The role of manganese in NAFLD remains poorly understood. However, the NHANES database offers valuable data on blood manganese levels and metabolic status for 6278 subjects in the United States, facilitating the study of this relationship.
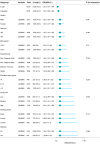
Methods: To investigate the relationship between blood manganese (Mn) levels and NAFLD, we conducted a t-test to compare Mn levels between participants with and without NAFLD. Participants were categorized into quartiles based on their blood Mn levels. We then employed multiple logistic regression analysis and sensitivity analyses to further examine the Mn-NAFLD relationship.
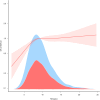
Results: The NAFLD group had a significantly higher blood manganese level (10.0 ± 3.7 μg/L, P < 0.05) than the control group. Stratifying 6278 subjects by blood manganese quartiles showed increased NAFLD odds in higher quartiles (Q2-Q4) vs. Q1 (ORs: 1.49, 1.37, 1.49). The Mn-NAFLD relationship followed an inverted L-shaped curve, peaking at 8.52 μg/L.
Conclusions: Elevated levels of manganese in the blood have been shown to be associated with an increase in the risk of NAFLD, and blood manganese values can be utilized as a marker for assessing NAFLD.
Keywords: Blood manganese; NAFLD; NHANES.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Blood manganese and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a high manganese exposure area in China.J Health Popul Nutr. 2023 Nov 6;42(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s41043-023-00467-2. J Health Popul Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37926847 Free PMC article.
-
Serum manganese and its association with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: findings from NHANES.Front Nutr. 2025 Mar 28;12:1527207. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1527207. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40225343 Free PMC article.
-
Blood manganese and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A cohort-based case-control study.Chemosphere. 2022 Jan;287(Pt 4):132316. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132316. Epub 2021 Sep 27. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 34592210
-
Cotinine exposure enhances the association of blood manganese and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in American children: a cross-sectional study.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 19;14(1):24593. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75298-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39426991 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Serum Zinc and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Advanced Liver Fibrosis: NHANES 2011-2016.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Mar;203(3):1305-1316. doi: 10.1007/s12011-024-04261-x. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 38861177
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

