The Role of Neutrophil CD11b Compared to Neutrophil CD64 as an Early Diagnostic, Monitoring, and Prognostic Sepsis Marker in Neonatal ICUs: Case-Control-Methodological Study
- PMID: 40224545
- PMCID: PMC11991832
- DOI: 10.1155/bmri/7206112
The Role of Neutrophil CD11b Compared to Neutrophil CD64 as an Early Diagnostic, Monitoring, and Prognostic Sepsis Marker in Neonatal ICUs: Case-Control-Methodological Study
Abstract
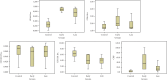
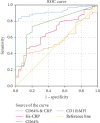
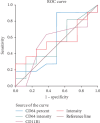
Background: Early diagnosis and treatment of neonatal sepsis are crucial to cut off its major medical consequences: lifelong morbidities, neurodevelopmental disabilities, and a high number of neonatal mortalities. Aim of the Work: This study is aimed at determining the diagnostic and prognostic performance of CD11b as a sepsis biomarker for detecting neonatal sepsis at early stages compared to nCD64 and the other conventional sepsis parameters. Methods: Two hundred eleven neonates were enrolled from three Egyptian neonatal ICUs (NICUs), and they were classified into two main groups: the control group (n = 101) and the sepsis group (n = 110). Enrolled neonates were subjected to full sepsis screening, including complete blood count (CBC), C-reactive protein (CRP), blood cultures, and flow cytometry analysis for both CD64 and CD11b on the neutrophil surface (results represented as a percentage (percent) and mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) units for either biomarker). Results: nCD64% (median = 44.15%) was significantly enhanced in the sepsis group compared to the controls (median = 25%), achieving 90.8% specificity, 92.8% sensitivity, and AUC = 0.894, respectively. CD64 MFI and CD11b MFI could differentiate between sepsis and control groups but with low undesirable diagnostic performance (sensitivity: 72.5% and 59.1%; specificity: 54.4% and 69.4%; AUC: 0.634 and 0.144, respectively). CD11b% could not discriminate between sepsis and control neonates (sensitivity and specificity of 31.8% and 73.6%, respectively) with an AUC of 0.405. hs-CRP had moderate diagnostic performance, achieving sensitivity and specificity of 69% and 78.15%, respectively, and AUC = 0.586. ROC analysis showed that combined hs-CRP and CD64% results had the highest sensitivity and specificity in the current study, being 93.9% and 97.2%, with AUC = 0.938, respectively. Conclusion: CD64%, CD64 MFI, CD11b MFI, and hs-CRP are increased in neonates with sepsis comparable to the controls. CD64% has a superior diagnostic performance comparable to nCD11b and hs-CRP. Combined nCD64 with hs-CRP measurement can provide rapid and accurate diagnostic modality for sepsis diagnosis in correlation with the patient's clinical condition and context with the results of other hematological indices; neutrophil CD64 can be routinely applicable in NICUs for better sepsis management. It is statistically evident that nCD11b is less ideal compared to nCD64 as a diagnostic, prognostic, or monitoring sepsis marker.
Keywords: biomarkers; diagnostic; inflammatory; neonates; neutrophil CD11b; neutrophil CD64; sepsis.
Copyright © 2025 Heba E. Hashem et al. BioMed Research International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Valuable Role of Neutrophil CD64 and Highly Sensitive CRP Biomarkers for Diagnostic, Monitoring, and Prognostic Evaluations of Sepsis Patients in Neonatal ICUs.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Aug 7;2020:6214363. doi: 10.1155/2020/6214363. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32832553 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Diagnostic, Prognostic, Predictive, and Monitoring Role of Neutrophil CD11b and Monocyte CD14 in Neonatal Sepsis.Dis Markers. 2021 Oct 14;2021:4537760. doi: 10.1155/2021/4537760. eCollection 2021. Dis Markers. 2021. PMID: 34691286 Free PMC article.
-
The Utility of Neutrophil CD64 and Presepsin as Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Monitoring Biomarkers in Neonatal Sepsis.Int J Microbiol. 2020 Nov 1;2020:8814892. doi: 10.1155/2020/8814892. eCollection 2020. Int J Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33204274 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy of neutrophil CD64 for neonatal sepsis.Ital J Pediatr. 2016 Jun 7;42(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13052-016-0268-1. Ital J Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27268050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is neutrophil CD11b a special marker for the early diagnosis of sepsis in neonates? A systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2019 May 1;9(4):e025222. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025222. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31048432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sastry S. A., Deepashree R. Essentials of Hospital Infection Control . Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers; 2019.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

