Exploring the Potential of Mitochondria-Targeted Drug Delivery for Enhanced Breast Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 40224721
- PMCID: PMC11991819
- DOI: 10.1155/ijbc/3013009
Exploring the Potential of Mitochondria-Targeted Drug Delivery for Enhanced Breast Cancer Therapy
Abstract
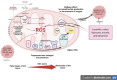
Breast cancer stands as the utmost prevalent malignancy in women, impacting the epithelial tissue of the breast and often displaying resistance to effective treatment due to its diverse molecular and histological features. Current treatment modalities may exhibit decreasing efficacy over time and can lead to disease progression. The mitochondria, a crucial organelle responsible for cellular metabolism and energy supply, stand highly sensitive to both heat and reactive oxygen species, presenting an assuring target for photodynamic and photothermal therapies (PTTs) in cancer cure. The employment of nanodrug carriers for combination deliveries holds promise in addressing challenges related to drug degradation and off-target toxicity. By circumventing the reticuloendothelial system, nanocarriers bolster the drug's bioavailability at the intended site and ensure controlled codelivery of multiple drugs, thereby maintaining the normal pharmacokinetic features and the regular pharmacodynamic characteristics of different therapeutic mechanisms. The precision and efficacy of this innovative technology have revolutionized drug delivery, substantially enhancing treatment effectiveness. In the pursuit of targeting mitochondrial modifications in cancer cells, various combination therapies such as photodynamic therapy (PDT), PTT, and chemodynamic therapy (CDT) have been explored. These therapies have improved the efficiency of mitochondria-targeted cancer treatment due to their advantageous properties of minimal toxicity, noninvasiveness, reduced drug resistance, and a safer profile. Our review article provides an exhaustive overview of alterations in the mitochondrial environment in BC, their impact on BC development, potential mitochondrial targets for BC treatment, nanotherapeutic approaches for targeting mitochondria, and the limitations of these approaches.
Keywords: breast cancer; immunological properties; mitochondria; nanotechnology.
Copyright © 2025 Yalda Ghazizadeh et al. International Journal of Breast Cancer published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Photodynamic Therapy Induced Mitochondrial Targeting Strategies for Cancer Treatment: Emerging Trends and Insights.Mol Pharm. 2024 Apr 1;21(4):1591-1608. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.3c01185. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Mol Pharm. 2024. PMID: 38396330 Review.
-
A dual-targeted hyaluronic acid-gold nanorod platform with triple-stimuli responsiveness for photodynamic/photothermal therapy of breast cancer.Acta Biomater. 2019 Jan 1;83:400-413. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.11.026. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 30465921
-
Nanoscale strides: exploring innovative therapies for breast cancer treatment.RSC Adv. 2024 Apr 29;14(20):14017-14040. doi: 10.1039/d4ra02639j. eCollection 2024 Apr 25. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38686289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondria-Targeted Nanomedicine for Enhanced Efficacy of Cancer Therapy.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Aug 19;9:720508. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.720508. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34490227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mito-Bomb: Targeting Mitochondria for Cancer Therapy.Adv Mater. 2021 Oct;33(43):e2007778. doi: 10.1002/adma.202007778. Epub 2021 Sep 12. Adv Mater. 2021. PMID: 34510563 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

