Examining the Relationship between Workplace Fun and Innovative Behavior among Nurses: The Mediating Effect of Innovation Support and Affective Commitment
- PMID: 40224838
- PMCID: PMC11919014
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/9629172
Examining the Relationship between Workplace Fun and Innovative Behavior among Nurses: The Mediating Effect of Innovation Support and Affective Commitment
Abstract
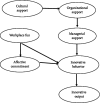
Aim: This study investigated the role of cultural, organizational, and managerial support, workplace fun, affective commitment, innovative behavior with innovative output, and also the mediating role of innovative behavior in the framework of a causal model.
Background: Innovation is the driving force of development in hospitals, and the quality of healthcare is closely related to hospital innovation. Today, nurses with innovative behaviors are the biggest asset of any hospital because they are involved in any improvement and progress.
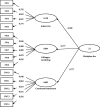
Methods: This descriptive cross-sectional correlational study was conducted using causal modeling methods, including path analysis and structural equation modeling. Using the proportional stratified sampling method, 321 nurses from Ardabil teaching hospitals were included in the study. Data were collected by standard demographic characteristics, innovative behaviors, innovative support, workplace fun, and affective commitment questionnaires. Partial least square structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) was used to test the conceptual model using PLS-SMART 2 software.
Results: Cultural support had a positive and significant effect on innovative behavior by affecting organizational support and then managerial support. In addition, workplace fun had a positive and significant effect on innovative behavior directly and indirectly through the mediating role of affective commitment. Finally, innovative behavior also had a positive and significant effect on nurses' innovative output.
Conclusion: Supervisors and managers can adopt the organizational and managerial support approach to improve the nurses' innovative behaviors. Workplace fun will also improve nurses' innovative behaviors and affective commitment, thereby increasing their innovative output. Implications for Nursing Management. By adopting organizational and managerial support for nurses' innovative behaviors, managers should take measures that promote workplace fun and affective commitment to improve nurses' innovative output by encouraging innovative behaviors.
Copyright © 2024 Maryam Hashemian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest..
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of workplace fun on Chinese nurse innovative behaviour: The intermediary function of affective commitment.J Nurs Manag. 2021 Oct;29(7):2250-2259. doi: 10.1111/jonm.13387. Epub 2021 Jul 18. J Nurs Manag. 2021. PMID: 34053146
-
Appreciative Leadership, Workplace Belongingness, and Affective Commitment of Nurses: The Mediating Role of Job Crafting.J Nurs Manag. 2024 Jul 5;2024:2311882. doi: 10.1155/2024/2311882. eCollection 2024. J Nurs Manag. 2024. PMID: 40224827 Free PMC article.
-
The boundary-spanning behavior of nurses: The role of support and affective organizational commitment.Health Care Manage Rev. 2020 Apr/Jun;45(2):130-140. doi: 10.1097/HMR.0000000000000210. Health Care Manage Rev. 2020. PMID: 30045100
-
Nurses' perception of empowerment and its relationship with organizational commitment and trust in teaching hospitals in Iran.J Nurs Manag. 2019 Jul;27(5):1020-1029. doi: 10.1111/jonm.12766. Epub 2019 Apr 10. J Nurs Manag. 2019. PMID: 30848036
-
Innovation in Nursing Practice: A Scoping Review.ANS Adv Nurs Sci. 2023 Oct-Dec 01;46(4):E115-E131. doi: 10.1097/ANS.0000000000000464. Epub 2022 Nov 15. ANS Adv Nurs Sci. 2023. PMID: 36317833
Cited by
-
Assessing the relationship between supervisor knowledge sharing and innovative behaviors among clinical nurses: the mediating role of organizational learning.BMC Nurs. 2025 May 12;24(1):508. doi: 10.1186/s12912-025-03165-y. BMC Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40355859 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mutonyi B. R., Slåtten T., Lien G., González-Piñero M. The impact of organizational culture and leadership climate on organizational attractiveness and innovative behavior: a study of Norwegian hospital employees. BMC Health Services Research . 2022;22(1):p. 637. doi: 10.1186/s12913-022-08042-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lukes M., Stephan U. Measuring employee innovation: a review of existing scales and the development of the innovative behavior and innovation support inventories across cultures. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior and Research . 2017;23(1):136–158. doi: 10.1108/ijebr-11-2015-0262. - DOI
-
- Sönmez B., İspir Ö, Önal M., Emiralioğlu R., editors. Nursing Forum . Hoboken, NJ, USA: Wiley Online Library; 2019. Turkish psychometric properties of the innovative behavior inventory and innovation support inventory: a model analysis on nurses. - PubMed
-
- Chan S. C. The antecedents of workplace fun in the hospitality industry: a qualitative study. Journal of Human Resources in Hospitality and Tourism . 2019;18(4):425–440. doi: 10.1080/15332845.2019.1626794. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

