Identification of novel neutrophil-extracellular-traps-related genes as biomarkers for breast cancer prognosis and immunotherapy
- PMID: 40224973
- PMCID: PMC11985209
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-24-1826
Identification of novel neutrophil-extracellular-traps-related genes as biomarkers for breast cancer prognosis and immunotherapy
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer (BC) ranks as one of the most prevalent malignancies among women globally. This study aimed to explore the involvement of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs)-related genes (NETRGs) in BC pathogenesis, highlighting the critical role of NETs.
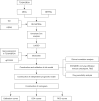
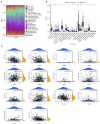
Methods: Differentially expressed NETRGs (DE-NETRGs) were identified by intersecting BC vs. control differentially expressed genes (DEGs) with the NETRG gene set from The Cancer Genome Atlas breast cancer (TCGA-BRCA) and GSE42568 datasets. Functional analysis elucidated their biological roles. Prognostic biomarkers were selected using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) and Cox regression, generating a predictive model, of which its prognostic predictive ability was evaluated through the Kaplan-Meier (KM) survival curve and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, and verified it in the test set and the validation set. Subsequently, the clinicopathological features were incorporated into the risk model for Cox independent prognostic analysis, and a nomogram was constructed to verify the predictive performance of the model. Finally, the mechanism of action of the biomarkers in BC was explored through immune infiltration, immunotherapy, and drug sensitivity. The biomarker expression validated by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).
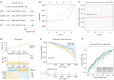
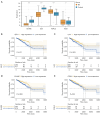
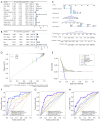
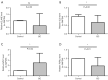
Results: Functional analysis revealed 37 DE-NETRGs associated with leukocyte migration and the Interleukin (IL)-17 signaling pathway. Four biomarkers [F2RL2, AZU1, IL33, neutrophil elastase (ELANE)] were used to construct the prognostic model and it was validated by the test set and the validation set. The KM curve showed significant differences in prognosis between the high- and low-risk group, while the ROC curve showed that the model had good predictive performance. Radiation, age, tumor stage, pathologic N, and risk scores were identified as independent prognostic factors. Subgroups based on risk scores exhibited distinct immune cell infiltration patterns, with the risk score positively correlated with M0 macrophages and resting mast cells. The high-risk group demonstrated lower Tumor Immune Dysfunction and Exclusion (TIDE) scores. Drug sensitivity varied between risk subgroups, and qRT-PCR confirmed the expression of ELANE and IL33.
Conclusions: This study has reported four biomarkers related to BC prognosis, namely F2RL2, AZU1, IL33, and ELANE. Our study has offered new potential biomarkers for prognosis and has identified therapeutic targets for the treatment and prognosis prediction in BC patients.
Keywords: Breast cancer (BC); Riskmodel; immunotherapy; neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs); prognosis.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-24-1826/coif). Z.H. reports the funding from Guangxi Natural Science Foundation Project (No. 2024GXNSFBA010024) and Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Health Commission (No. Z-A20230008). J.Y. reports the funding from the Major Project of Science and Technology of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (No. Guike-AA22096018). The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
