Mobile health (mHealth) technologies for fall prevention among older adults in low-middle income countries: bibliometrics, network analysis and integrative review
- PMID: 40225124
- PMCID: PMC11985854
- DOI: 10.3389/fdgth.2025.1559570
Mobile health (mHealth) technologies for fall prevention among older adults in low-middle income countries: bibliometrics, network analysis and integrative review
Abstract
Introduction: mHealth technologies offer promising solutions to reduce the incidence of falls among older adults. Unfortunately, publications on their application to Low-Middle Income Countries (LMIC) settings have not been collectively examined.
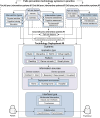
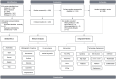
Methods: A triadic research design involving bibliometrics, network analysis, and model-based integrative review was conducted to process articles (n = 22) from 629 publications extracted from major databases using keywords related to mHealth, falls prevention, and LMIC. The web-based application Covidence and stand-alone VosViewer software were used to process data following previously published review standards.
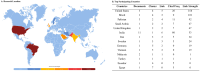
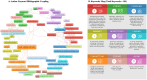
Results: Published articles in the field feature multidisciplinary authorships from multiple scholars in the domains of health and technology. Network analysis revealed the most prominent stakeholders and keyword clusters related to mHealth technology features and applications in healthcare. The papers predominantly focused on the development of mHealth technology, usability, and affordances and less on the physiologic and sociologic attributes of technology use. mHealth technologies in low and middle-income countries are mostly smartphone-based, static, and include features for home care settings with fall detection accuracy of 86%-99.62%. Mixed reality-based mobile applications have not yet been explored.
Conclusion: Overall, key findings and information from the articles highlight a gradually advancing research domain. Outcomes reinforce the need to expand the focus of mHealth investigations to include emerging technologies, update current technology models, create a more human-centered technology design, test mHealth technologies in the clinical setting, and encourage continued cooperation between and among researchers from various fields and environments.
Keywords: bibliometrics; fall prevention; fall risk; integrative review; low-middle income countries; mHealth; network analysis; older adults.
© 2025 Dino, Thiamwong, Xie, Malacas, Hernandez, Balbin, Vital, Rivero and Xi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human-Centered Design of Mobile Health Apps for Older Adults: Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2022 Jan 14;10(1):e29512. doi: 10.2196/29512. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2022. PMID: 35029535 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping mHealth research: a decade of evolution.J Med Internet Res. 2013 May 21;15(5):e95. doi: 10.2196/jmir.2430. J Med Internet Res. 2013. PMID: 23697600 Free PMC article.
-
Multidisciplinary Contributions and Research Trends in eHealth Scholarship (2000-2024): Bibliometric Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jun 16;27:e60071. doi: 10.2196/60071. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40522718 Free PMC article.
-
Tools for Evaluating the Content, Efficacy, and Usability of Mobile Health Apps According to the Consensus-Based Standards for the Selection of Health Measurement Instruments: Systematic Review.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2021 Dec 1;9(12):e15433. doi: 10.2196/15433. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2021. PMID: 34855618 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for preventing and reducing the use of physical restraints for older people in all long-term care settings.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jul 28;7(7):CD007546. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007546.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37500094 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Population Prospects—Population Division—United Nations. (2024). Available at: https://population.un.org/wpp/ (Accessed October 29, 2024).
-
- United Nations. World Population Ageing 2019 Highlights. New York: United Nations; (2019). 10.18356/9df3caed-en - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources