Double Diabetes: A Converging Metabolic and Autoimmune Disorder Redefining the Classification and Management of Diabetes
- PMID: 40225541
- PMCID: PMC11992394
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.80495
Double Diabetes: A Converging Metabolic and Autoimmune Disorder Redefining the Classification and Management of Diabetes
Abstract
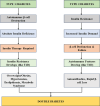
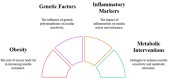
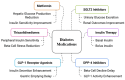
This review explores the pathophysiology, clinical implications, and management of double diabetes. The increasing prevalence of obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and genetic predisposition has blurred the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, leading to diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. Double diabetes presents with overlapping symptoms from both diabetes types, making accurate diagnosis crucial. Biomarkers, such as C-peptide levels, autoantibody testing, and insulin resistance markers, help differentiate double diabetes from classic diabetes subtypes. Early intervention is necessary because of the condition's elevated risk of microvascular and macrovascular consequences, such as retinopathy, nephropathy, and cardiovascular disease. Effective management integrates pharmacological and lifestyle approaches. Metformin, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, and insulin therapy adjustments all boost glycemic control and metabolic results. Additionally, structured exercise, dietary modifications, and weight management are essential for reducing insulin resistance and preserving beta-cell activity. The potential of precision medicine, artificial intelligence (AI)-driven healthcare, and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) offers promising advancements for personalized treatment strategies. Future research should focus on targeted immunotherapies, genetic profiling, and refined clinical guidelines to improve early detection and individualized treatment, with long-term outcomes. The review emphasizes the need for a multidisciplinary approach in managing double diabetes, ensuring early diagnosis, optimized treatment, and improved metabolic health to mitigate long-term complications.
Keywords: autoimmune dysfunction; beta-cell dysfunction; double diabetes; insulin resistance; metabolic syndrome; precision medicine.
Copyright © 2025, Chaudhary et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Diabetes Care. 2022;45:0–38.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
