A Rare Cause of Infection Following Total Knee Arthroplasty: Abiotrophia defectiva Linked to Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections
- PMID: 40225546
- PMCID: PMC11987417
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.80460
A Rare Cause of Infection Following Total Knee Arthroplasty: Abiotrophia defectiva Linked to Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections
Abstract
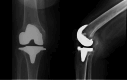
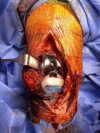
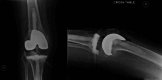
Abiotrophia defectiva (A. defectiva) is a rare cause of prosthetic joint infection (PJI), and its role in surgical site infections remains unclear. A 66-year-old female developed an A. defectiva infection two years following primary right total knee arthroplasty (TKA). The patient presented with fever, knee pain, and urinary tract infection (UTI). She had a history of recurrent UTIs, likely contributing to the hematogenous spread of the pathogen. Knee aspiration was initially negative; however, subsequent cultures detected A. defectiva. The PJI was managed with surgical debridement, removal of prosthetic components, and a dynamic antibiotic spacer. We highlight the challenges associated with A. defectiva PJIs. The pathogen's fastidiousness complicates identification, and its biofilm formation on prosthetic materials makes eradication difficult. Despite its rarity, A. defectiva should be considered as a possible cause of PJIs, particularly in patients with recurrent UTIs. Early recognition and aggressive management are crucial.
Keywords: abiotrophia defectiva; case report; prosthetic joint infection; total knee arthroplasty; urinary tract infection.
Copyright © 2025, Nooh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Abiotrophia defectiva and Granulicatella: A Literature Review on Prosthetic Joint Infection and a Case Report on A. defectiva PJI and Concurrent Native Valve Endocarditis.Microorganisms. 2025 May 12;13(5):1113. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13051113. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40431286 Free PMC article.
-
Abiotrophia defectiva as a Rare Causative Agent of Periprosthetic Total Knee Arthroplasty Infections: A Case Report and Literature Review.J Lab Physicians. 2020 Dec;12(3):219-221. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1720942. Epub 2020 Nov 23. J Lab Physicians. 2020. PMID: 33268940 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a periprosthetic joint infection by Abiotrophia defectiva years after total knee arthroplasty.Arthroplast Today. 2019 Jan 31;5(1):49-51. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2018.12.002. eCollection 2019 Mar. Arthroplast Today. 2019. PMID: 31020021 Free PMC article.
-
A woman with infectious endocarditis caused by Abiotrophia defectiva.Intern Med. 2004 Oct;43(10):1000-4. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.43.1000. Intern Med. 2004. PMID: 15575256 Review.
-
Total knee arthroplasty infection due to Abiotrophia defectiva.J Med Microbiol. 2002 Oct;51(10):899-902. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-51-10-899. J Med Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12435072 Review.
Cited by
-
Abiotrophia defectiva and Granulicatella: A Literature Review on Prosthetic Joint Infection and a Case Report on A. defectiva PJI and Concurrent Native Valve Endocarditis.Microorganisms. 2025 May 12;13(5):1113. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13051113. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40431286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lawson PA. Lactic Acid Bacteria: Biodiversity and Taxonomy. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley; 2014. The genus Abiotrophia; pp. 75–80.
-
- Antimicrobial susceptibility of Abiotrophia adiacens and Abiotrophia defectiva. Tuohy MJ, Procop GW, Washington JA. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000;38:189–191. - PubMed
-
- Abiotrophia defectiva endocarditis. Pinkney JA, Nagassar RP, Roye-Green KJ, Ferguson T. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25519863/ BMJ Case Rep. 2014;2014 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abiotrophia defectiva as a cause of infective endocarditis with embolic complications in children. Song SH, Ahn B, Choi EH, et al. Infection. 2020;48:783–790. - PubMed
-
- Bacterial endocarditis caused by Abiotrophia defectiva in a healthy adult: a case report with literature review. Je H, Song D, Chang CL. Ann Clin Microbiol. 2019;22:23–27.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
