Measurement of Work-Life Balance: A Scoping Review with a Focus on the Health Sector
- PMID: 40225624
- PMCID: PMC11919065
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/3666224
Measurement of Work-Life Balance: A Scoping Review with a Focus on the Health Sector
Abstract
Background: There is an agreement on the importance of measuring work-life balance, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the available tools to do so are not sufficient to address all dimensions, contexts, and professions.
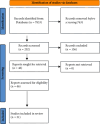
Aim: The article reviews existing instruments that have been widely utilised to tap into the breadth and depth of work-life balance. Evaluation. This is a perspective scoping review guided by PRISMA-ScR guidelines. Articles reporting on the measurement of work-life balance were reviewed. The authors performed the review based on agreed-upon search terms, inclusion and exclusion criteria, search databases, and the data extraction process. Key Issues. The existing tools appear to have divergent underpinning theoretical models, factors, structural/psychometric properties, and the number of accumulated citations. The existing tools also varied in terms of their target sector, with limited tools available for the analysis of work-life balance among healthcare professionals. We argue that while the existing tools provide a general base for the work-life balance measurement, it would be imperative to adjust those tools to the specific cultural and professional contexts. Future work-life balance measures should consider the changes imposed by atypical or disruptive events that have the potential to alter work-life balance, such as in the case of the COVID-19 pandemic. The onus is on researchers and policymakers to work collaboratively in each context to adapt, implement, and evaluate those tools as they become integrated into the matrix of labour market assessments in the future.
Conclusions: The article highlighted current gaps and improvement opportunities in the work-life balance measurement field. Implications for Healthcare and Nursing Management. The maintenance of work-life balance will remain an issue for years to come. Ensuring comprehensive and context-specific measurements would be essential to guide the evidence-based recommendations necessary to support the workforce across the various sectors of the economy in the future.
Copyright © 2023 Mohamad Alameddine et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gregg P. Black Death to Industrial Revolution . Harrap London: A social and economic History of England; 1976.
-
- Cohn S. K., Cohn S. K. The Black Death Transformed . Arnold London: Disease and Culture in Early Renaissance Europe; 2003.
-
- Bhumika. Challenges for work-life balance during COVID-19 induced nationwide lockdown: exploring gender difference in emotional exhaustion in the Indian setting. Gender in Management . 2020;35(7/8):705–718. doi: 10.1108/GM-06-2020-0163. - DOI
-
- International Labour Organization. Teleworking During the COVID-19 Pandemic and Beyond: A Practical Guide . Geneva, Switzerland: ILO; 2020.
-
- Brough P., Holt J., Bauld R., Biggs A., Ryan C. The ability of work—life balance policies to influence key social/organisational issues. Asia Pacific Journal of Human Resources . 2008;46(3):261–274. doi: 10.1177/1038411108095758. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous