Effect of tirofiban arterial injection on neurological and endothelial function in acute ischemic stroke patients beyond the thrombolysis time window
- PMID: 40226001
- PMCID: PMC11982856
- DOI: 10.62347/BGRM4102
Effect of tirofiban arterial injection on neurological and endothelial function in acute ischemic stroke patients beyond the thrombolysis time window
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of arterial tirofiban injection in patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) beyond the thrombolysis time window.
Methods: In this retrospective single-center study, clinical data were analyzed from 230 AIS patients treated at the First Hospital of Yulin between July 2021 and January 2023. Patients were divided into two groups: the observation group (n=102) treated with tirofiban combined with dual antiplatelet therapy, and the control group (n=128) that received dual antiplatelet therapy alone. Post-treatment follow-up evaluated neurological function, endothelial function, and safety using the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS), modified Rankin Scale (mRS), and Barthel Index (BI). Endothelial function was assessed by measuring levels of endothelin-1 (ET-1), nitric oxide (NO), and von Willebrand factor (vWF). Baseline characteristics, treatment protocols, and complications were analyzed to ensure the reliability and scientific rigor of the results.
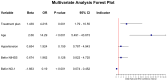
Results: Compared to the control group, the observation group demonstrated significant improvements in NIHSS, mRS, and BI scores, indicating enhanced neurological function and self-care ability. Endothelial markers (ET-1, NO, and vWF) also significantly improved in the observation group, suggesting a beneficial effect on endothelial function. The overall efficacy rate at 90 days was 86.72% in the observation group, significantly higher than the 74.50% in the control group (P<0.05). In terms of safety, there were no significant differences in the incidence of adverse events between the two groups, indicating that tirofiban is well-tolerated. Multivariate analysis identified age, treatment protocol, and baseline NO levels as independent factors affecting the 90-day prognosis, underscoring the importance of individualized treatment strategies for AIS patients.
Conclusion: Arterial injection of tirofiban significantly improves neurological and endothelial function in AIS patients beyond the thrombolysis time window while maintaining a favorable safety profile. These findings support the use of tirofiban in patients who are ineligible for intravenous thrombolysis or endovascular treatment.
Keywords: Tirofiban; acute ischemic stroke; endothelial function; neurological function; safety; thrombolysis.
AJTR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety and efficacy of tirofiban after intravenous thrombolysis with urokinase in patients with acute ischemic stroke.Front Neurol. 2025 Mar 6;16:1529331. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1529331. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40115384 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of intravenous tirofiban in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke patients with early neurological deterioration.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022 Dec;47(12):2350-2359. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13816. Epub 2022 Dec 2. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022. PMID: 36461632 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and preliminary efficacy of intravenous tirofiban in acute ischemic stroke patient without arterial occlusion on neurovascular imaging studies.J Neurol Sci. 2017 Dec 15;383:175-179. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2017.10.041. Epub 2017 Oct 26. J Neurol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29246609
-
Early tirofiban administration for patients with acute ischemic stroke treated with intravenous thrombolysis or bridging therapy: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2022 Nov;222:107449. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2022.107449. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2022. PMID: 36162161
-
Tirofiban Combination Therapy for Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Brain Behav. 2025 Jun;15(6):e70508. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70508. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40495442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walter K. What is acute ischemic stroke? JAMA. 2022;327:885. - PubMed
-
- Ma Q, Li R, Wang L, Yin P, Wang Y, Yan C, Ren Y, Qian Z, Vaughn MG, McMillin SE, Hay SI, Naghavi M, Cai M, Wang C, Zhang Z, Zhou M, Lin H, Yang Y. Temporal trend and attributable risk factors of stroke burden in China, 1990-2019: an analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Public Health. 2021;6:e897–e906. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huo X, Ma G, Tong X, Zhang X, Pan Y, Nguyen TN, Yuan G, Han H, Chen W, Wei M, Zhang J, Zhou Z, Yao X, Wang G, Song W, Cai X, Nan G, Li D, Wang AY, Ling W, Cai C, Wen C, Wang E, Zhang L, Jiang C, Liu Y, Liao G, Chen X, Li T, Liu S, Li J, Gao F, Ma N, Mo D, Song L, Sun X, Li X, Deng Y, Luo G, Lv M, He H, Liu A, Zhang J, Mu S, Liu L, Jing J, Nie X, Ding Z, Du W, Zhao X, Yang P, Liu L, Wang Y, Liebeskind DS, Pereira VM, Ren Z, Wang Y, Miao Z ANGEL-ASPECT Investigators. Trial of endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke with large infarct. N Engl J Med. 2023;388:1272–1283. - PubMed
-
- Li S, Gu HQ, Li H, Wang X, Jin A, Guo S, Lu G, Che F, Wang W, Wei Y, Wang Y, Li Z, Meng X, Zhao X, Liu L, Wang Y RAISE Investigators. Reteplase versus alteplase for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2024;390:2264–2273. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
