Intravenous injection of 0.5 μg/kg dexmedetomidine during plasma resection of tonsil adenoids can reduce the incidence of delirium and hemodynamics in children
- PMID: 40226004
- PMCID: PMC11982874
- DOI: 10.62347/TWCY6801
Intravenous injection of 0.5 μg/kg dexmedetomidine during plasma resection of tonsil adenoids can reduce the incidence of delirium and hemodynamics in children
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of different doses of dexmedetomidine on delirium and hemodynamics after plasma resection of adenoids in children.
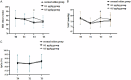
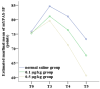
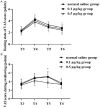
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on the clinical data of 80 children who underwent plasma adenoidectomy of tonsil at the Pediatric Hospital of Fudan University from January 2022 to December 2023. The patients were divided into normal saline group, 0.1 μg/kg dexmedetomidine group, and 0.5 μg/kg dexmedetomidine group according to the dose of dexmedetomidine injected intravenously. Hemodynamic changes, modified Yale Preoperative Anxiety Scale (mYPAS-SF) scores, pharyngeal pain (at rest and during swallowing), coagulation function, and postoperative adverse reactions were compared at T0, 10 min after dexmedetomidine pumping (T1), extubation (T2), recovery (T3), 2 h after returning to ward (T4), 12 h after returning to ward (T5) and 24 h after returning to ward (T6), respectively.
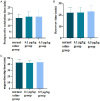
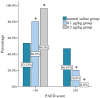
Results: There were no significant differences in extubation time, recovery time, or unguardianship time among the three groups (P>0.05). The incidence of postoperative delirium was significantly lower in the 0.1 μg/kg dexmedetomidine group and 0.5 μg/kg dexmedetomidine group compared to the normal saline group (P<0.05), with the 0.5 μg/kg group showing better results. At T2, heart rate (HR) and mean arterial pressure (MAP) levels were significantly lower in 0.1 μg/kg group and 0.5 μg/kg dexmedetomidine group than those in normal saline group (P<0.05). The mYPAS-SF score was significantly lower in the 0.1 μg/kg group and 0.5 μg/kg dexmedetomidine groups than that of the normal saline group at T3, T4 and T5 (P<0.05). The score of pharyngeal pain during swallowing was significantly lower in the 0.5 μg/kg dexmedetomidine group at T5 than that of the normal saline group and 0.1 μg/kg dexmedetomidine group (P<0.05). Coagulation values (PT, APTT, and TT) were significantly altered 36 hours post-surgery, with PT, APTT, and TT increasing, while fibrinogen (FIB) decreased (P<0.05). Postoperative nasopharyngeal hemorrhage occurred in one case and nausea/vomiting in two cases in the saline group. No anesthesia-related adverse reactions were observed in the dexmedetomidine group.
Conclusion: Intravenous injection of 0.5 μg/kg dexmedetomidine during plasma resection of tonsillar adenoids can reduce the incidence of postoperative delirium, stabilize hemodynamics, relieve postoperative anxiety and pharyngeal pain, with minimal impacts on coagulation function. Additionally, it reduces the incidence of adverse reactions, making it a promising option for clinical use.
Keywords: Dexmedetomidine; plasma resection of tonsil adenoid; postoperative delirium.
AJTR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Hao X, Wang JZ, Qu H. Effect of resection of adenoids and/or tonsil on the immune indexes in children with obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019;54:830–836. - PubMed
-
- Abdallah BM, Elshoeibi AM, ElTantawi N, Arif M, Hourani RF, Akomolafe AF, Hamwi MN, Mahmood FR, Saracoglu KT, Saracoglu A, Chivese T. Comparison of postoperative pain in children after maintenance anaesthesia with propofol or sevoflurane: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2024;133:93–102. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Urbánek L, Urbánková P, Satinský I, Trávníček T, Penka I, Hruda J. Postoperative delirium. Rozhl Chir. 2023;102:381–386. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
