A neuropathic pain scale is effective in identifying neuropathic pain
- PMID: 40226007
- PMCID: PMC11982898
- DOI: 10.62347/BXRB6015
A neuropathic pain scale is effective in identifying neuropathic pain
Abstract
Objective: To explore the application value of a Neuropathic Pain Questionnaire (NPQ) in screening for neuropathic pain (NP).
Methods: Using a prospective study approach, patients with chronic pain treated and hospitalized in Quanzhou First Hospital between September 2020 and December 2023 were chosen as study subjects. Participants were screened using NPQ and then divided into a neuropathic pain group (NP group) and a non-neuropathic pain group (NNP group) based on NPQ's results. The baseline demographic data and disease causes were evaluated using Cronbach's alpha coefficient and Guttman split-half coefficient to assess internal consistency. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was plotted, and the area under curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) were assessed.
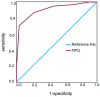
Results: A total of of 121 patients were included, with 61 cases in the NP group and 60 cases in NNP group. There were no substantial differences between the NP group and the NNP group in terms of age, gender, education level, payment method of medical treatment, pain duration, average pain duration, or level of pain (all P > 0.05). The NP group had a substantially higher NPQ score (8.67±1.21) than the NNP group (6.31±1.34) (P < 0.05). The primary causes of NP in the NP group were postherpetic neuralgia (26.23%), diabetic neuropathy (21.31%), and central post-stroke pain (18.03%). The NPQ demonstrated strong reliability, with a Cronbach's alpha coefficient of 0.843 and a Guttman split-half coefficient of 0.822. The ROC analysis showed an AUC of 0.907 (95% CI, 0.853-0.961), with a sensitivity of 86.90%, specificity of 78.30%, PPV of 80.30%, and NPV of 85.45%.
Conclusion: NPQ is a reliable and effective tool for identifying neuropathic pain. Its high sensitivity and specificity, coupled with strong diagnostic performance, suggest that it can be used as a screening tool for neuropathic pain.
Keywords: Neuropathic pain questionnaire; application effect; neuropathic pain; screening.
AJTR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Scholz J, Finnerup NB, Attal N, Aziz Q, Baron R, Bennett MI, Benoliel R, Cohen M, Cruccu G, Davis KD, Evers S, First M, Giamberardino MA, Hansson P, Kaasa S, Korwisi B, Kosek E, Lavand’homme P, Nicholas M, Nurmikko T, Perrot S, Raja SN, Rice ASC, Rowbotham MC, Schug S, Simpson DM, Smith BH, Svensson P, Vlaeyen JWS, Wang SJ, Barke A, Rief W, Treede RD Classification Committee of the Neuropathic Pain Special Interest Group (NeuPSIG) The IASP classification of chronic pain for ICD-11: chronic neuropathic pain. Pain. 2019;160:53–59. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bouhassira D. Neuropathic pain: definition, assessment and epidemiology. Rev Neurol (Paris) 2019;175:16–25. - PubMed
-
- Venda Nova C, Zakrzewska JM, R Baker S, Ni Riordain R. Patient reported outcome measures in trigeminal neuralgia - A systematic review of psychometric performance. Eur J Pain. 2021;25:1449–1461. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous