Effect of regorafenib combined with immunotherapy and arterial chemoembolization on the survival of patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study
- PMID: 40226031
- PMCID: PMC11982895
- DOI: 10.62347/BXYO6569
Effect of regorafenib combined with immunotherapy and arterial chemoembolization on the survival of patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the effect of combining regorafenib with immunotherapy, and further adding transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), on the survival rates of patients suffering from advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted on clinical data from 219 patients with advanced HCC treated from January 2019 to December 2020 at Zhangzhou Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University. Patients were divided into two groups: regorafenib combined with immunotherapy (Group A; n = 106) and regorafenib combined with immunotherapy plus TACE (Group B; n = 113). Assessment included baseline characteristics, serum indicators, treatment response, adverse events, progression-free survival (PFS), quality of life and overall survival (OS).
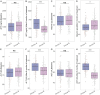
Results: Six months after treatment, Group B demonstrated a significant decrease in α-fetoprotein (AFP) levels (P < 0.001), Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels (P < 0.001), and aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) levels (P < 0.001), along with a significant increase in albumin (ALB) levels (P = 0.010) compared to Group A. The addition of TACE resulted in higher partial response rates (PR) (P = 0.044), disease control rates (DCR) (P = 0.005), overall response rates (ORR) (P = 0.014), improved 1- and 2-year survival rates (P = 0.019, 0.025), and 6-month PFS rates (P = 0.003). However, this combination therapy was related to a higher incidence of grade 3-4 adverse events.
Conclusion: Regorafenib combined with immunotherapy plus TACE may lead to improved short-term survival outcomes in advanced HCC patients, albeit with an increased risk of adverse events as well as possible effects on quality of life. These findings emphasize the complexity of treatment decisions in advanced HCC.
Keywords: Regorafenib; arterial chemoembolization; hepatocellular carcinoma; immunotherapy; retrospective study; survival outcomes.
AJTR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Study on safety and efficacy of regorafenib combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma after first-line targeted therapy.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Jun;13(3):1248-1254. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-395. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35837179 Free PMC article.
-
The second-line treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with CalliSpheres drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization combined with regorafenib: A safety and efficacy analysis.Ir J Med Sci. 2024 Jun;193(3):1215-1222. doi: 10.1007/s11845-024-03611-x. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Ir J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38300460
-
Gelatin sponge microparticles for transarterial chemoembolization combined with regorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma: a single-center retrospective study.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Dec;13(6):3183-3192. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-1170. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36636092 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization combined with targeted therapy and immunotherapy versus with targeted monotherapy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 May 3;103(18):e38037. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038037. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38701263 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization combined with tyrosine kinase inhibitors and immune checkpoint inhibitors versus tyrosine kinase inhibitors and immune checkpoint inhibitors alone in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2025 Apr 7;23(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12957-025-03788-0. World J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40197348 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakada S, Allard MA, Lewin M, Awad S, Dahbi N, Nitta H, Cunha AS, Castaing D, Vibert E, Cherqui D, Miyazaki M, Ohtsuka M, Adam R. Ischemic cholangiopathy following transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy: an underestimated and devastating complication. J Gastrointest Surg. 2020;24:2517–2525. - PubMed
-
- Cucchetti A, Casadei Gardini A. Understanding surrogate measures of overall survival after trans-arterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2021;41:891–893. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
