Construction and validation of a nomogram model to predict mortality risk in patients with acute diquat poisoning
- PMID: 40226039
- PMCID: PMC11982848
- DOI: 10.62347/XXIL7895
Construction and validation of a nomogram model to predict mortality risk in patients with acute diquat poisoning
Abstract
Objective: To analyze the risk factors for mortality in patients with acute diquat (DQ) poisoning and construct a nomogram prediction model for clinical assessment and treatment.
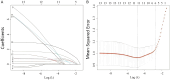
Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed on the clinical data of 110 patients with acute DQ poisoning who were admitted from March 2022 to April 2024. The enrolled patients were divided into a training set of 80 cases and a validation set of 30 cases. A survival group and a death group were established, with death within 30 days as the endpoint. Among these, in the training group, there were 67 cases in the survival group and 13 cases in the death group. This study further analyzed and compared the baseline and clinical data of the two groups of patients, screened potential risk factors using Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression, and determined independent risk factors through multivariate logistic regression analysis. A nomogram predictive model was constructed and validated based on the validation set.
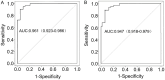
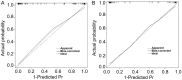
Results: Using LASSO regression, this study screened 13 possible risk factors. The dosage of DQ, gastric lavage rate, medication to hospital admission time, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, blood potassium, creatinine, urea, partial pressure of oxygen, urinary DQ concentration, Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) score, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score, and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II score were found to predict death significantly after acute DQ poisoning. This study further constructed the nomogram predictive model and validated the predictive performance of this model by using a validation set. The Area Under the Curve (AUC) of the training set was 0.961, and that of the validation set was 0.947. The calibration curve of the training and validation sets showed good prediction results of the model, and the calibration curve tended to approach the ideal curve.
Conclusion: This study constructed a nomogram model to predict mortality risk in patients with acute DQ poisoning. Clinicians will have a clearer and intuitive understanding of the prognosis of patients, so as to enhance the treatment of patients and optimize the allocation of medical resources.
Keywords: Diquat; mortality; nomogram; poisoning; risk prediction model.
AJTR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Establishment of a nomogram prediction model for 28-day mortality of septic shock patients based on routine laboratory data mining].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Nov;36(11):1127-1132. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240202-00108. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 39697015 Chinese.
-
[Establishment and validation of a sepsis 28-day mortality prediction model based on the lactate dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio in patients with sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Nov;36(11):1140-1146. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20231012-00865. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 39697017 Chinese.
-
[Development and validation of a prognostic model for patients with sepsis in intensive care unit].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023 Aug;35(8):800-806. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20230103-00003. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023. PMID: 37593856 Chinese.
-
[Analysis of risk factors for prognosis of patients with acute paraquat intoxication].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015 Nov;27(11):906-10. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015. PMID: 27132458 Chinese.
-
Construction of a risk prediction model of diquat poisoning based on clinical indicators.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2025 Jan;55(1):55-62. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2024.2433242. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39688342 Review.
References
-
- Fu G, Duan Y, Yi W, Zhang S, Liang W, Li H, Yan H, Wu B, Fu S, Zhang J, Zhang G, Wang G, Liu Y, Xu S. A rapid and reliable immunochromatographic strip for detecting paraquat poinsoning in domestic water and real human samples. Environ Pollut. 2022;315:120324. - PubMed
-
- Mao Z, Yu Y, Sun H, Xie W, Zhao H, Jiang Q, Sun Y, Cao Y, Chen F. Development and validation of a sensitive and high throughput UPLC-MS/MS method for determination of paraquat and diquat in human plasma and urine: application to poisoning cases at emergency departments of hospitals. Forensic Toxicol. 2022;40:102–110. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe D, Sonoda S, Ohta H. Simultaneous determination of water-soluble herbicides using hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Forensic Toxicol. 2024;42:1–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
