Genomic analyses reveal presence of extensively drug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from clinical samples in Guizhou province, China, 2019-2023
- PMID: 40226105
- PMCID: PMC11987122
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1532036
Genomic analyses reveal presence of extensively drug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from clinical samples in Guizhou province, China, 2019-2023
Abstract
Background: The emergence of extensively drug-resistant (XDR) Salmonella in humans poses a significant public health and therapeutic challenge. However, limited data are available on XDR Salmonella isolates from Guizhou province, China. This study aimed to investigate the molecular epidemiology and resistance patterns of XDR Salmonella isolates from clinical samples in this region.
Methods: A total of 931 Salmonella isolates were screened for XDR isolates through antimicrobial susceptibility testing. These XDR isolates were subjected to whole-genome sequencing (WGS) and bioinformatic analysis to further systematically investigating the molecular epidemiology and resistance patterns of XDR Salmonella isolates.
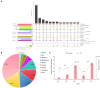
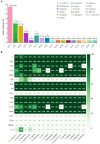
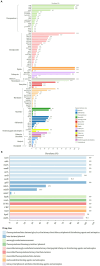
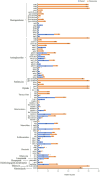
Results: Between 2019 and 2023, 931 Salmonella isolates were collected from clinical samples in Guizhou. Of these isolates, 51 (5.5%) were identified as XDR and classified into 16 serovars. Among the serovars, 15 corresponded to a specific sequence type, except for S. Typhimurium serovars. The predominant serovars, S. 1,4,[5],12:i:-, S. Enteritidis, and S. Kentucky, were divided into ST34, ST11, and ST198, respectively. Genomic analysis showed that all XDR isolates harbored at least eight antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs) and multidrug efflux pumps. Highly prevalent point mutations in gyrA (D87 and S83) and parC (S80I) were detected, along with eight plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance (PMQR) genes. The qnrS1 gene was the most common (43.1%), followed by oqxA, aac-(6')-lb-cr variant, qnrB4, qnrS2, qnrA1, qepA2, and oqxB. The predominant β-lactamase gene was blaTEM-1 (54.9%), and blaCTX-M-55 (35.3%) was the most prevalent extended-spectrum β-lactamase subtype. Notably, blaNDM-1 gene was identified for the first time in Salmonella from Guizhou, and one S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- isolate contained the mcr-1.1 gene. ARGs profiles varied by serovars, with S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- isolates carrying the highest number. Ten plasmid types were identified, predominantly IncHI2/IncHI2A (47.5%). Key resistance genes such as tetA, PMQR, blaCTX-M , mcr-1.1, and blaNDM-1 were located on IncHI2/IncHI2A plasmids. Notably, 75.0% of the conjugative plasmids belonged to IncHI2/IncHI2A, indicating that horizontal gene transfer through conjugation facilitates ARGs dissemination. Core genome multilocus sequence typing (cgMLST) analysis revealed significant genetic diversity, with 39 core genome sequence types (cgSTs) identified and no evidence of outbreaks.
Conclusion: The rising prevalence of XDR Salmonella in Guizhou province is concerning. Initial whole-genome sequencing (WGS) data provide critical insights for understanding and controlling XDR Salmonella infections, aiding public health officials in identifying emerging threats and trends.
Keywords: Salmonella; antimicrobial resistance genes; extensively drug-resistant; plasmid; whole-genome sequencing.
Copyright © 2025 Wen, Wu, You, Wei, Wang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
BlaTEM-positive Salmonella enterica serovars Agona and Derby are prevalent among food-producing animals in Chongqing, China.Front Microbiol. 2023 May 25;14:1011719. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1011719. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37303807 Free PMC article.
-
Genome analysis of colistin-resistant Salmonella isolates from human sources in Guizhou of southwestern China, 2019-2023.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jan 29;16:1498995. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1498995. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39944652 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiological analysis and characterization of Salmonella and ciprofloxacin-resistant Escherichia coli isolates recovered from retail fresh vegetables in Shaanxi Province, China.Int J Food Microbiol. 2023 Feb 16;387:110053. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2022.110053. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Int J Food Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36521241
-
Serovar and sequence type distribution and phenotypic and genotypic antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella originating from pet animals in Chongqing, China.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jul 2;12(7):e0354223. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03542-23. Epub 2024 May 17. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38757951 Free PMC article.
-
Poultry production as the main reservoir of ciprofloxacin- and tigecycline-resistant extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky ST198.2-2 causing human infections in China.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Sep 28;89(9):e0094423. doi: 10.1128/aem.00944-23. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37610223 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Overcoming Multidrug Resistance in E. coli and Salmonella Isolates from Nile Tilapia: Synergistic Effects of Novel Antibiotic Combinations.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Jun 29. doi: 10.1007/s12033-025-01462-0. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40581898
References
-
- Abd El-Aziz N. K., Tartor Y. H., Gharieb R. M. A., Erfan A. M., Khalifa E., Said M. A., et al. . (2021). Extensive drug-resistant Salmonella enterica isolated from poultry and humans: prevalence and molecular reterminants behind the co-resistance to ciprofloxacin and tigecycline. Front. Microbiol. 12:738784. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.738784, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akinyemi K. O., Fakorede C. O., Linde J., Methner U., Wareth G., Tomaso H., et al. . (2023). Whole genome sequencing of Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from humans, animals, and the environment in Lagos, Nigeria. BMC Microbiol. 23:164. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-02901-1, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Algammal A. M., El-Tarabili R. M., Abd El-Ghany W. A., Almanzalawi E. A., Alqahtani T. M., Ghabban H., et al. . (2023). Resistance profiles, virulence and antimicrobial resistance genes of XDR S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium. AMB Express 13:110. doi: 10.1186/s13568-023-01615-x, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

