Establishing the Median and 95% Effective Doses of Oliceridine for Immediate Post-Surgical Analgesia Following Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Double-Blind, Sequential Dose-Finding Study
- PMID: 40226130
- PMCID: PMC11992992
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S505079
Establishing the Median and 95% Effective Doses of Oliceridine for Immediate Post-Surgical Analgesia Following Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Double-Blind, Sequential Dose-Finding Study
Abstract
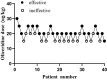
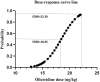
Background: This investigation aimed to establish the optimal dosing parameters of oliceridine for postoperative pain control in laparoscopic cholecystectomy (LC) procedures. Using Dixon and Massey's up-and-down sequential allocation method, the median effective dose (ED50) and the dose required for 95% effective dose (ED95) were determined, alongside an evaluation of the agent's safety profile.
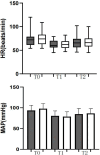
Methods: In this prospective trial, 82 participants scheduled for LC were enrolled and randomly assigned to receive either oliceridine or saline (control). Prior to surgical incision, the intervention group received varying doses of intravenous oliceridine, while control subjects received equivalent volumes of saline solution. Post-surgical pain management involved standardized multimodal analgesic protocols for both cohorts. Baseline demographic data was documented for all participants. Pain evaluations using the 11-point verbal numeric rating scale (NRS) at 15 min, 30 min, and 2h post-extubation. Using Dixon's up-and-down methodology, the ED50 and ED95 were determined. Hemodynamic variables were tracked and pain levels quantified throughout the procedure. The study protocol included monitoring post-anesthetic recovery characteristics and documenting adverse effects.
Results: Probability unit regression analysis indicated that the ED50 of oliceridine for the prevention of early postoperative pain was calculated to be 18.45 µg/kg (95% CI: 16.85-19.82 µg/kg), while the ED95 was determined to be 22.39 µg/kg (95% CI: 20.75-26.98 µg/kg). Statistical analysis showed comparable rates of adverse events between study groups (p > 0.05). Additional analyses demonstrated similar outcomes between oliceridine and control cohorts regarding hemodynamic stability, and adverse effect profiles. Pain management satisfaction assessment at 24 hours post-LC revealed high approval rates in the oliceridine group, with 90% of patients (36/40, p=0.31) and 97.5% of surgeons (39/40, p=0.03) expressing satisfaction, regardless of administered dose.
Conclusion: Our findings establish that for early postoperative pain management, oliceridine demonstrates optimal therapeutic efficacy at an ED50 of 18.45 ug/kg, with the ED95 determined to be 22.39 ug/kg.
Keywords: ED50; ED95; laparoscopic cholecystectomy; oliceridine; postoperative pain.
© 2025 Cao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effective Dose of Oliceridine Fumarate Co-Administered with Remimazolam in Suppressing Gastroscope Insertion Responses for Adults.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jun 10;19:5033-5041. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S527586. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40524805 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The ED50 and ED95 of esketamine for preventing early postoperative pain in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a prospective, double-blinded trial.BMC Anesthesiol. 2023 Nov 25;23(1):385. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02357-w. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 38001477 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
APOLLO-2: A Randomized, Placebo and Active-Controlled Phase III Study Investigating Oliceridine (TRV130), a G Protein-Biased Ligand at the μ-Opioid Receptor, for Management of Moderate to Severe Acute Pain Following Abdominoplasty.Pain Pract. 2019 Sep;19(7):715-731. doi: 10.1111/papr.12801. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Pain Pract. 2019. PMID: 31162798 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Tolerability of different doses of oliceridine versus traditional opioids in acute pain management: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 3;15(1):11470. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95978-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40181183 Free PMC article.
-
Safety evaluation of oliceridine for the management of postoperative moderate-to-severe acute pain.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2021 Nov;20(11):1291-1298. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2021.1965989. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2021. PMID: 34370562 Review.
References
-
- on behalf of the SAGES Safe Cholecystectomy Task Force, Pucher PH, Brunt LM, Davies N, et al. Outcome trends and safety measures after 30 years of laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a systematic review and pooled data analysis. Surg Endosc. 2018;32(5):2175–2183. doi:10.1007/s00464-017-5974-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hilvering B, Draaisma WA, Van Der Bilt JDW, Valk RM, Kofman KE, Consten ECJ. Randomized clinical trial of combined preincisional infiltration and intraperitoneal instillation of levobupivacaine for postoperative pain after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Br J Surg. 2011;98(6):784–789. doi:10.1002/bjs.7435 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

