Salidroside inhibits the invasion and migration of colorectal cancer cells by regulating MMP-12 and WNT signaling pathway
- PMID: 40226472
- PMCID: PMC11982737
- DOI: 10.62347/KELA7583
Salidroside inhibits the invasion and migration of colorectal cancer cells by regulating MMP-12 and WNT signaling pathway
Abstract
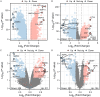
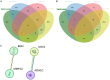
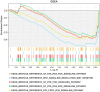
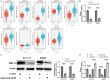
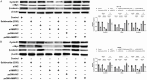
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a prevalent and highly lethal malignancy, with current therapeutic efficacy limited by the tumor's high invasiveness and metastatic potential. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and the WNT (Wingless/Integrated) signaling pathway play key roles in the invasion and metastasis of CRC. Salidroside, a natural compound, has demonstrated inhibitory effects in several cancers, but its precise molecular mechanism in CRC cells remains unclear. This study aims to investigate the antitumor effect of salidroside on CRC and its molecular mechanism in influencing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by regulating MMP-12 and the WNT signaling pathway. The effects of salidroside on CRC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion were evaluated through in vitro experiments using HCT-116 and SW620 cell lines. The antitumor effects of salidroside were validated using CCK-8, wound healing, and Transwell assays. Expression changes of MMP-12, WNT signaling-related proteins (e.g., β-catenin, GSK-3β), and EMT markers (e.g., E-cadherin, Vimentin) after salidroside treatment were measured by qRT-PCR and Western Blot. Additionally, bioinformatics analysis was performed using TCGA and GEO databases in combination with the BEST online tool to identify differentially expressed genes, followed by GSEA enrichment analysis. Salidroside showed significant antiproliferative and inhibitory effects on the migration and invasion of CRC cells. In vitro experiments demonstrated that salidroside significantly inhibited CRC cell proliferation and reduced their migration and invasion capabilities. qRT-PCR and Western Blot analyses showed that salidroside significantly downregulated MMP-12 expression and led to changes in the expression of WNT signaling and EMT-related proteins, specifically downregulating β-catenin, upregulating E-cadherin, and downregulating Vimentin. Furthermore, bioinformatics analysis indicated that MMP-12 plays a crucial role in salidroside-mediated CRC inhibition, further supporting its potential as a key target. In conclusion, salidroside suppresses CRC invasion and migration by downregulating MMP-12 and modulating the WNT signaling pathway, thereby inhibiting the EMT process. These findings suggest that salidroside holds potential as a therapeutic agent for CRC, offering a novel approach to CRC treatment.
Keywords: MMP-12; Salidroside; WNT signaling pathway; colon cancer; invasion; migration.
AJCR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures





References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Kratzer TB, Jemal A, Miller KD, Nash S, Wiggins C, Redwood D, Smith R, Siegel RL. Cancer statistics for American Indian and Alaska Native individuals, 2022: including increasing disparities in early onset colorectal cancer. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73:120–146. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:229–263. - PubMed
-
- Argilés G, Tabernero J, Labianca R, Hochhauser D, Salazar R, Iveson T, Laurent-Puig P, Quirke P, Yoshino T, Taieb J, Martinelli E, Arnold D ESMO Guidelines Committee. Electronic address: clinicalguidelines@esmo.org. Localised colon cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2020;31:1291–1305. - PubMed
-
- Wei M, Huang X, Liao L, Tian Y, Zheng X. SENP1 decreases RNF168 phase separation to promote DNA damage repair and drug resistance in colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2023;83:2908–2923. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
