Unveiling the impact of ERAP1 and ERAP2 on migration, angiogenesis and ER stress response
- PMID: 40226591
- PMCID: PMC11985534
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1564649
Unveiling the impact of ERAP1 and ERAP2 on migration, angiogenesis and ER stress response
Abstract
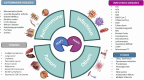
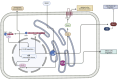
Recent studies have investigated the key roles exerted by ERAP1 and ERAP2 in maintaining cellular homeostasis, emphasizing their functions beyond traditional antigen processing and presentation. In particular, genetic variants of these IFNγ-inducible aminopeptidases significantly impact critical cellular pathways, including migration, angiogenesis, and autophagy, which are essential in immune responses and disease processes. ERAP1's influence on endothelial cell migration and VEGF-driven angiogenesis, along with ERAP2's role in managing stress-induced autophagy via the UPR, highlights their importance in cellular adaptation to stress and disease outcomes, including autoimmune diseases, cancer progression, and infections. By presenting recent insights into ERAP1 and ERAP2 functions, this review underscores their potential as therapeutic targets in immune regulation and cellular stress-response pathways.
Keywords: ER stress; ERAPs; autopaghy; cell biology; cell migration.
Copyright © 2025 Saulle, Vitalyos, D’Agate, Clerici and Biasin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

References
-
- Batool S., Javed M. R., Aslam S., Noor F., Javed H. M. F., Seemab R., et al. (2022). Network pharmacology and bioinformatics approach reveals the multi-target pharmacological mechanism of fumaria indica in the treatment of liver cancer. Pharm. (Basel) 15, 654. 10.3390/ph15060654 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

