Enhanced TLR7-dependent production of type I interferon by pDCs underlies pandemic chilblains
- PMID: 40227192
- PMCID: PMC11995862
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20231467
Enhanced TLR7-dependent production of type I interferon by pDCs underlies pandemic chilblains
Abstract
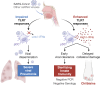
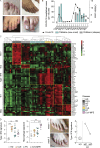
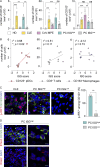
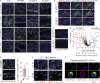
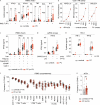
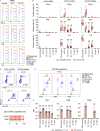
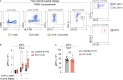
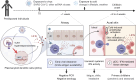
Outbreaks of chilblains were reported during the COVID-19 pandemic. Given the essential role of type I interferon (I-IFN) in protective immunity against SARS-CoV-2 and the association of chilblains with inherited type I interferonopathies, we hypothesized that excessive I-IFN responses to SARS-CoV-2 might underlie the occurrence of chilblains in this context. We identified a transient I-IFN signature in chilblain lesions, accompanied by an acral infiltration of activated plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs). Patients with chilblains were otherwise asymptomatic or had mild disease without seroconversion. Their leukocytes produced abnormally high levels of I-IFN upon TLR7 stimulation with agonists or ssRNA viruses-particularly SARS-CoV-2-but not with DNA agonists of TLR9 or the dsDNA virus HSV-1. Moreover, the patients' pDCs displayed cell-intrinsic hyperresponsiveness to TLR7 stimulation regardless of TLR7 levels. Inherited TLR7 or I-IFN deficiency confers a predisposition to life-threatening COVID-19. Conversely, our findings suggest that enhanced TLR7 activity in predisposed individuals could confer innate, pDC-mediated, sterilizing immunity to SARS-CoV-2 infection, with I-IFN-driven chilblains as a trade-off.
© 2025 Saidoune et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Albarrán-Juárez, J., Iring A., Wang S., Joseph S., Grimm M., Strilic B., Wettschureck N., Althoff T.F., and Offermanns S.. 2018. Piezo1 and Gq/G11 promote endothelial inflammation depending on flow pattern and integrin activation. J. Exp. Med. 215:2655–2672. 10.1084/jem.20180483 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arkin, L.M., Moon J.J., Tran J.M., Asgari S., O’Farrelly C., Casanova J.L., Cowen E.W., Mays J.W., Singh A.M., Drolet B.A., et al. 2021. From your nose to your toes: A review of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 pandemic‒associated pernio. J. Invest. Dermatol. 141:2791–2796. 10.1016/j.jid.2021.05.024 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology
- Schlumberger Foundation
- French Foundation for Medical Research
- Université Paris-Saclay
- Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale
- CRI5801/Carson Family Foundation
- ITMO Cancer of Aviesan
- R01 AI163029/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- Fisher Center for Alzheimer's Research Foundation
- INCa
- 101057100/HORIZON-HLTH-2021-DISEASE-04
- European Society for Immunodeficiencies
- George Mason University
- Rockefeller University
- Meyer Foundation
- R01 AI091707/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 4078P0_198470/SNSF_/Swiss National Science Foundation/Switzerland
- ALTF 380-2018/European Molecular Biology Organization
- Thrasher Research Fund
- UL1 TR001866/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI161444/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- Leenaards Foundation
- Battersea & Bowery Advisory Group
- R01AI163029/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- Grandir - Fonds de solidarité pour l'enfance
- ANR-10-IAHU-01/Agence Nationale de la Recherche
- Bawd Foundation
- 824110/European Union's Horizon 2020
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- Square Foundation
- CRI/Cancer Research Institute/United States
- UL1TR001866/Clinical and Translational Science Award
- Université de Paris
- G. Harold and Leila Y. Mathers Charitable Foundation
- Fondation du Souffle
- SCOR Corporate Foundation for Science
- St. Giles Foundation
- U19 AI111825/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- General Atlantic Foundation
- JPB Foundation
- MESRI-COVID-19/French Ministry of Higher Education, Research, and Innovation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

