Microbial-Derived Antioxidants in Intestinal Inflammation: A Systematic Review of Their Therapeutic Potential
- PMID: 40227262
- PMCID: PMC11939483
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox14030321
Microbial-Derived Antioxidants in Intestinal Inflammation: A Systematic Review of Their Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
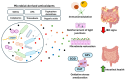
The potential of microbial-derived antioxidants to modulate intestinal inflammation is increasingly recognized, which is especially important in inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). Oxidative stress, a major contributor to chronic intestinal inflammation, is the result of an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body's antioxidant defenses. This systematic review explores the role of microbial-derived antioxidants in alleviating IBD. Among the main findings are certain compounds, such as exopolysaccharides (EPS) and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which have demonstrated their ability to neutralize ROS and strengthen the integrity of the intestinal barrier, thereby attenuating inflammatory responses. These antioxidants offer the dual benefit of mitigating oxidative stress and rebalancing the gut microbiota, which is often disrupted in IBD. Evidence from preclinical and clinical studies provides a better understanding of the mechanisms involved in the effects of these microbial antioxidants. Conventional treatments for IBD primarily focus on immune modulation. In this context, the integration of microbial-derived antioxidants could offer a complementary approach by addressing both oxidative damage and gut dysbiosis. Further research and clinical trials are essential to establish standardized treatment guidelines and clarify the long-term efficacy of these promising therapeutic agents.
Keywords: SCFAs; dysbiosis; gut; inflammation; microbial-derived antioxidants; microbiome; postbiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Li J., Simmons A.J., Hawkins C.V., Chiron S., Ramirez-Solano M.A., Tasneem N., Kaur H., Xu Y., Revetta F., Vega P.N., et al. Identification and multimodal characterization of a specialized epithelial cell type associated with Crohn’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2024;15:7204. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51580-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Luceri C., Bigagli E., Agostiniani S., Giudici F., Zambonin D., Scaringi S., Ficari F., Lodovici M., Malentacchi C. Analysis of Oxidative Stress-Related Markers in Crohn’s Disease Patients at Surgery and Correlations with Clinical Findings. Antioxidants. 2019;8:378. doi: 10.3390/antiox8090378. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shen C., Luo Z., Ma S., Yu C., Lai T., Tang S., Zhang H., Zhang J., Xu W., Xu J. Microbe-Derived Antioxidants Protect IPEC-1 Cells from H(2)O(2)-Induced Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Tight Junction Protein Disruption via Activating the Nrf2 Pathway to Inhibit the ROS/NLRP3/IL-1beta Signaling Pathway. Antioxidants. 2024;13:533. doi: 10.3390/antiox13050533. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

