Roles of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 in Muscle Wasting and Osteopenia in Mice with Hyponatremia
- PMID: 40227313
- PMCID: PMC11996959
- DOI: 10.1007/s00223-025-01369-7
Roles of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 in Muscle Wasting and Osteopenia in Mice with Hyponatremia
Abstract
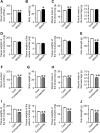
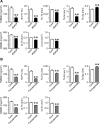
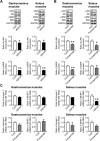
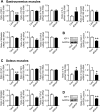
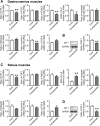
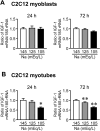
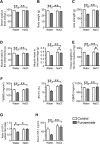
Hyponatremia is associated with sarcopenia and osteoporosis in elderly individuals. Skeletal muscle releases myokines, which affect distant organs, including bone. However, the detailed mechanisms by which hyponatremia influences muscle and bone remain unclear. We herein investigated the effects of hyponatremia on muscle, bone, and myokines linking muscle to bone in mice treated with 1-desamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin (dDAVP) or furosemide, which induce hyponatremia. Muscle mass and bone mineral density (BMD) were analyzed 8 weeks after the administration of dDAVP or furosemide. dDAVP significantly reduced grip strength, but did not affect tissue weights of gastrocnemius or soleus muscles of mice. Furosemide significantly decreased muscle mass, tissue weights of gastrocnemius and soleus muscles, and grip strength in mice. dDAVP and furosemide decreased trabecular BMD, trabecular bone volume, and cortical BMD at the femurs. Among myokines linking muscle to bone, hyponatremia reduced expression of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1 in gastrocnemius and soleus muscles and serum IGF-1 levels in mice. In simple regression analyses, serum IGF-1 levels were positively related to muscle IGF-1 expression, trabecular bone volume, and cortical BMD in mice. The administration of sodium chloride solution to mice ameliorated the decreases in grip strength, muscle mass, trabecular bone volume, cortical BMD, and the levels of muscle and circulating IGF-1 in furosemide-treated mice. The present study demonstrated that hyponatremia induces muscle and bone loss as well as a decrease in muscle IGF-1 expression in mice. The present findings suggest that IGF-1 might be related to muscle wasting and bone loss induced by hyponatremia in mice.
Keywords: Bone loss; Hyponatremia; IGF-1; Muscle wasting.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors Naoyuki Kawao, AkihitoNishikawa, Daichi Matsumura, AyakaYamada, Takashi Ohira, Yuya Mizukami and Hiroshi Kaji declare that they have no conflict of interest. Ethical Approval: Animal experiments were performed in accordance with the guidelines of ARRIVE and the institutional rules for the use and care of laboratory animals at Kindai University. All experimental procedures on animals were approved by the Experimental Animal Welfare Committee of Kindai University (Permit number: KAME-2022-079). Research Involving Human and Animal Participants and Informed Consent: All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted. This study does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of irisin in androgen-deficient muscle wasting and osteopenia in mice.J Bone Miner Metab. 2020 Mar;38(2):161-171. doi: 10.1007/s00774-019-01043-7. Epub 2019 Sep 7. J Bone Miner Metab. 2020. PMID: 31494773
-
Renal failure suppresses muscle irisin expression, and irisin blunts cortical bone loss in mice.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022 Feb;13(1):758-771. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12892. Epub 2022 Jan 7. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022. PMID: 34997830 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of elastase-induced emphysema on muscle and bone in mice.PLoS One. 2023 Jun 23;18(6):e0287541. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287541. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37352205 Free PMC article.
-
Role of irisin in effects of chronic exercise on muscle and bone in ovariectomized mice.J Bone Miner Metab. 2021 Jul;39(4):547-557. doi: 10.1007/s00774-020-01201-2. Epub 2021 Feb 10. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021. PMID: 33566209
-
Roles of natural products on myokine expression and secretion in skeletal muscle atrophy.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2024 Sep 1;355:114550. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2024.114550. Epub 2024 May 18. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 38768928 Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the Metabolic Pathways Between Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) and Sarcopenia.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 14;26(10):4673. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104673. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429815 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Verbalis JG, Goldsmith SR, Greenberg A, Korzelius C, Schrier RW, Sterns RH, Thompson CJ (2013) Diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of hyponatremia: expert panel recommendations. Am J Med 126:S1-42 - PubMed
-
- Radvanyi Z, Yoo EJ, Kandasamy P, Salas-Bastos A, Monnerat S, Refardt J, Christ-Crain M, Hayashi H, Kondo Y, Jantsch J, Rubio-Aliaga I, Sommer L, Wagner CA, Hediger MA, Kwon HM, Loffing J, Pathare G (2024) Extracellular sodium regulates fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) formation. J Biol Chem 300:105480 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoorn EJ, Rivadeneira F, van Meurs JB, Ziere G, Stricker BH, Hofman A, Pols HA, Zietse R, Uitterlinden AG, Zillikens MC (2011) Mild hyponatremia as a risk factor for fractures: the Rotterdam Study. J Bone Miner Res 26:1822–1828 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

