From Bench to Bedside: Translational Approaches to Cardiotoxicity in Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer, and Lymphoma Therapies
- PMID: 40227572
- PMCID: PMC11987928
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17071059
From Bench to Bedside: Translational Approaches to Cardiotoxicity in Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer, and Lymphoma Therapies
Abstract
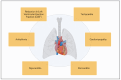
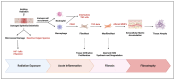
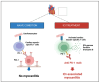
Cardiotoxicity represents a critical challenge in cancer therapy, particularly in the treatment of thoracic tumors, such as lung cancer and lymphomas, as well as breast cancer. These malignancies stand out for their high prevalence and the widespread use of cardiotoxic treatments, such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy. This work underscores the importance of preclinical models in uncovering the mechanisms of cardiotoxicity and developing targeted prevention and mitigation strategies. In vitro models provide valuable insights into cellular processes, enabling the observation of changes in cell viability and function following exposure to various drugs or ionizing radiation. Complementarily, in vivo animal models offer a broader perspective, allowing for evaluating of both short- and long-term effects and a better understanding of chronic toxicity and cardiac diseases. By integrating these approaches, researchers can identify potential mechanisms of cardiotoxicity and devise effective prevention strategies. This analysis highlights the central role of preclinical models in advancing knowledge of cardiotoxic effects associated with common therapeutic regimens for thoracic and breast cancers.
Keywords: cardiotoxicity; chemotherapy; immunotherapy; preclinical models; radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Miura K., Sano Y., Niho S., Kawasumi K., Mochizuki N., Yoh K., Matsumoto S., Zenke Y., Ikeda T., Nosaki K. Impact of concomitant medication on clinical outcomes in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A retrospective study. Thorac. Cancer. 2021;12:1983–1994. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lai E., Persano M., Dubois M., Spanu D., Donisi C., Pozzari M., Deias G., Saba G., Migliari M., Liscia N., et al. Drug-related toxicity in breast cancer patients: A new path towards tailored treatment?—A narrative review. Precis. Cancer Med. 2022;5:1–24. doi: 10.21037/pcm-21-38. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

