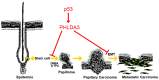
The Role of PHLDA3 in Cancer Progression and Its Potential as a Therapeutic Target
- PMID: 40227573
- PMCID: PMC11988131
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17071069
The Role of PHLDA3 in Cancer Progression and Its Potential as a Therapeutic Target
Abstract
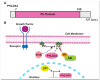
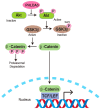
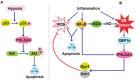
Pleckstrin homology-like domain family A, member 3 (PHLDA3) is a p53-regulated tumor suppressor protein that suppresses AKT-mediated survival and oncogenic signaling. The PHLDA3 gene has garnered significant attention due to its multifaceted roles in tumorigenesis, metastasis, and invasion. This review explores the complex interactions between PHLDA3 and key cellular processes involved in cancer, emphasizing its regulatory mechanisms and clinical relevance. PHLDA3 has been found to be a critical regulator of metastatic pathways, particularly through its influence on the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and in cellular invasion. Its interactions with pivotal signaling pathways, such as the Phosphoinositide 3-kinases/Protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT), p53, and Wnt/β-catenin pathways, highlight its multifunctional roles in various cancer types. Additionally, we discuss the potential of PHLDA3 as both a prognostic biomarker and a therapeutic target, offering new insights into its potential in treating advanced-stage malignancies. This review provides a detailed analysis of the role of PHLDA3 in cancer progression, including metastasis and invasion, underscoring its therapeutic potential.
Keywords: AKT pathway; PHLDA3; invasion; metastasis; p53; tumor progression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel R.L., Giaquinto A.N., Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024;74:12–49. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J., Colombet M., Soerjomataram I., Parkin D.M., Piñeros M., Znaor A., Bray F. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int. J. Cancer. 2021;149:778–789. - PubMed
-
- Ma S., Quan P., Yu C., Fan X., Yang S., Jia W., Yang X. PHLDA3 exerts an antitumor function in prostate cancer by down-regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway via inhibition of AKT. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021;571:66–73. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

