Effect of Tasurgratinib as an Orally Available FGFR1-3 Inhibitor on Resistance to a CDK4/6 Inhibitor and Endocrine Therapy in ER+/HER2- Breast Cancer Preclinical Models
- PMID: 40227585
- PMCID: PMC11988047
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17071084
Effect of Tasurgratinib as an Orally Available FGFR1-3 Inhibitor on Resistance to a CDK4/6 Inhibitor and Endocrine Therapy in ER+/HER2- Breast Cancer Preclinical Models
Abstract
Background: Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling plays a crucial role in several cellular functions in cancer cells. Tasurgratinib, formerly known as E7090, is an orally available FGF receptor (FGFR)1-3 selective inhibitor. Here, we present the effects of tasurgratinib on the resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors and endocrine therapy (ET) in a preclinical model.
Methods: Estrogen receptor (ER)+ breast cancer (BC) patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models harboring ESR1 wild-type or ESR1 mutation were used as animal models. An in vitro cell proliferation assay of ER+ BC cell lines treated with fulvestrant or palbociclib + fulvestrant was conducted in the presence of FGF2 and FGF10, with or without tasurgratinib.
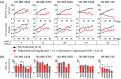
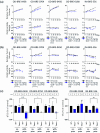
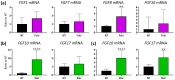
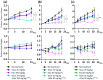
Results: Among five ER+ BC PDX models, OD-BRE-0438 and OD-BRE-0704 showed higher sensitivities to tasurgratinib with prior palbociclib + fulvestrant than without it. In these models, palbociclib + fulvestrant treatment upregulated the expression of several FGF ligand mRNAs. In vitro, FGF2 and FGF10 decreased the sensitivity to both fulvestrant and palbociclib + fulvestrant, which was restored by co-treatment with tasurgratinib. Consistently, fulvestrant + tasurgratinib and elacestrant + tasurgratinib showed antitumor activity in ER+ BC PDX models harboring ESR1 wild-type and ESR1 mutation, respectively. In these models, fulvestrant or elacestrant upregulated the expression of several FGF ligand mRNAs.
Conclusions: FGF signaling plays a role in resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors and ET in ER+ BC. Tasurgratinib has the potential to exhibit significant antitumor activity in combination with ET against ER+ BC via FGF signaling inhibition. These findings indicate the therapeutic potential of tasurgratinib in treating ER+ BC.
Keywords: CDK4/6 inhibitor; FGFR; breast cancer; endocrine therapy; tasurgratinib.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are employees of Eisai Co., Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Elacestrant demonstrates strong anti-estrogenic activity in PDX models of estrogen-receptor positive endocrine-resistant and fulvestrant-resistant breast cancer.NPJ Breast Cancer. 2022 Nov 29;8(1):125. doi: 10.1038/s41523-022-00483-1. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36446866 Free PMC article.
-
Elacestrant (RAD1901) exhibits anti-tumor activity in multiple ER+ breast cancer models resistant to CDK4/6 inhibitors.Breast Cancer Res. 2019 Dec 18;21(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1230-0. Breast Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31852484 Free PMC article.
-
Lasofoxifene as a potential treatment for aromatase inhibitor-resistant ER-positive breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 7;26(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s13058-024-01843-4. Breast Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38849889 Free PMC article.
-
Novel endocrine therapies: What is next in estrogen receptor positive, HER2 negative breast cancer?Cancer Treat Rev. 2023 Jun;117:102569. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2023.102569. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Cancer Treat Rev. 2023. PMID: 37146385 Review.
-
Clinical utility of fulvestrant in the treatment of breast cancer: a report on the emerging clinical evidence.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Aug 30;10:3083-3099. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S137772. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 30214302 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program. [(accessed on 18 December 2024)]; Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast-subtypes.html.
-
- Johnston S., Martin M., Di Leo A., Im S.-A., Awada A., Forrester T., Frenzel M., Hardebeck M.C., Cox J., Barriga S., et al. MONARCH 3 final PFS: A randomized study of abemaciclib as initial therapy for advanced breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2019;5:5. doi: 10.1038/s41523-018-0097-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beaver J.A., Amiri-Kordestani L., Charlab R., Chen W., Palmby T., Tilley A., Zirkelbach J.F., Yu J., Liu Q., Zhao L., et al. FDA Approval: Palbociclib for the Treatment of Postmenopausal Patients with Estrogen Receptor–Positive, HER2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015;21:4760–4766. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-15-1185. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

