Metabolite Changes Associated with Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 40227642
- PMCID: PMC11988049
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17071150
Metabolite Changes Associated with Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
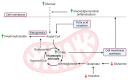
Introduction: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is insidious, with only 15-20% of those diagnosed suitable for surgical resection as it is either too advanced and has invaded local structures or has already spread to distant sites. The associated tumor microenvironment provides a protective shield which limits the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents, but also impairs the delivery of nutrients required for the PDAC cells. To compensate for this, metabolic adaptions occur to provide alternative sources of fuel. The aim of this study is to explore metabolomic differences between participants with resectable PDAC compared to healthy volunteers (HV). The objectives were to use nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and mass spectrometry (MS) to determine if resectable PDAC induces sufficient metabolic adaptations and variations which could be used to discriminate between the two groups.
Methods: Plasma samples were collected from fasted individuals with resectable PDAC (n = 23, median age 68 [IQR 56-75], 69.6% male) and HV (n = 24, median age 63 [IQR 58-71], 54.2% male). Samples were analyzed using NMR and the Biocrates MxP Quant 500 kit at University Hospital Southampton.
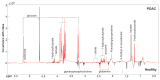
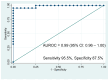
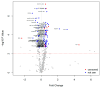
Results: NMR spectroscopy identified six independent metabolites that significantly discriminated between the PDAC and HV groups, including elevated plasma concentrations of 3-hydroxybutyrate and citrate, with decreased amounts of glutamine and histidine. MS analysis identified 84 metabolites with a significant difference between the PDAC and HV cohorts. The metabolites with a fold change (FC) > 1.5 in the PDAC population were conjugated bile acids (taurocholic acid, glycocholic acid, and glycochenodexoycholic acid).
Discussion: In conclusion, using metabolomics, biochemical differences between resectable PDAC and HV were detected. These differences indicate metabolic plasticity and utilization of alternative fuel sources.
Keywords: PDAC; adenocarcinoma; metabolite; metabolomics; pancreatic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R.L., Giaquinto A.N., Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024;74:12–49. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

