Effects of depression and anxiety symptoms on cognitive inhibition: A cross-sectional study of structural and functional MRI evidence
- PMID: 40228249
- PMCID: PMC11999389
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042000
Effects of depression and anxiety symptoms on cognitive inhibition: A cross-sectional study of structural and functional MRI evidence
Abstract
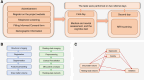
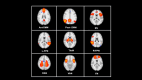
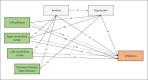
Evidence shows that depression and anxiety symptoms are associated with reduced cognitive inhibition. Nevertheless, the neural substrates responsible for the effects of depression and anxiety symptoms on cognitive inhibition are yet to be determined. This cross-sectional study adhered to the strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) checklist. Data from 242 participants from the Iranian brain imaging database were used in this study. To address the neural substrates of depression and anxiety responsible for inhibition, voxel-based morphometry (VBM) analysis and resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (RS-fMRI) were used. The depression anxiety stress scale was used to evaluate symptoms of depression and anxiety, and the Stroop test was used for cognitive inhibition. The behavioral results demonstrated that inhibition was significantly negatively correlated with depression and anxiety. The VBM results showed that depression was negatively correlated with gray matter (GM) volume in the left pallidum and the right cerebellum cortex. Additionally, anxiety negatively correlated with GM volume in the left and right cerebellum cortex. RS-fMRI results showed that the thalamus network was positively correlated with depression and anxiety. more importantly, mediation analysis revealed that the right cerebellum cortex and thalamic resting-state network through depression and anxiety had a total indirect effect on inhibition. Clarifying the neural substrates responsible for how depression and anxiety symptoms affect cognitive inhibition could have important implications for interventions aimed at supporting individuals' cognitive health.
Keywords: anxiety; cognitive inhibition; depression; resting‐state network; voxel‐based morphometry.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gray matter substrates of depressive and anxiety symptoms in idiopathic REM sleep behavior disorder.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2019 May;62:163-170. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.12.020. Epub 2018 Dec 17. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2019. PMID: 30616869
-
Distinct Patterns of Brain Atrophy associated with Mild Behavioral Impairment in Cognitively Normal Elderly Adults.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Jun 11;18(13):2950-2956. doi: 10.7150/ijms.60810. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34220322 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebellum abnormalities in vascular mild cognitive impairment with depression symptom patients: A multimodal magnetic resonance imaging study.Brain Res Bull. 2025 Feb;221:111213. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2025.111213. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Brain Res Bull. 2025. PMID: 39824229
-
[Grey matter concentration revealed by voxel-based morphometry in individuals with cognitive vulnerability to depression].Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017 Jun 28;42(6):667-672. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2017.06.012. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017. PMID: 28690225 Chinese.
-
Disrupted Balance of Gray Matter Volume and Directed Functional Connectivity in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2023;20(3):161-174. doi: 10.2174/1567205020666230602144659. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2023. PMID: 37278043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- MacLeod CM. The concept of inhibition in cognition. In: Inhibition in Cognition.; 2008. doi:10.1037/11587-001
-
- Joormann J. Cognitive inhibition and emotion regulation in depression. Curr Dir Psychol Sci. 2010;19:161–6.
-
- Barlow DH, Allen LB, Choate ML. Toward a unified treatment for emotional disorders. In: The Neurotic Paradox, Volume 1: Progress in Understanding and Treating Anxiety and Related Disorders.; 2020. doi:10.4324/9781315724539-12
-
- Richard-Devantoy S, Ding Y, Lepage M, Turecki G, Jollant F. Cognitive inhibition in depression and suicidal behavior: a neuroimaging study. Psychol Med. 2016;46:933. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

