Acute myocardial infarction after batroxobin treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Case report
- PMID: 40228268
- PMCID: PMC11999433
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042158
Acute myocardial infarction after batroxobin treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Case report
Abstract
Rationale: The drug batroxobin is utilized to enhance microcirculation by reducing fibrinogen levels, making it a treatment option for the acute stage of severe sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL). However, the efficacy of batroxobin defibrination remains controversial. It is crucial to also consider the potential thrombotic effects of batroxobin. This is the first report of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in patients after treatment for SSNHL with batroxobin, aiming to enhance its clinical safety profile.
Patient concerns: A 61-year-old male patient presented with severe SSNHL in the left ear. During hospitalization, the plasma fibrinogen level remained consistently low following batroxobin treatment and subsequently led to AMI.
Diagnoses: SSNHL, AMI.
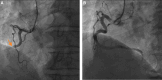
Interventions: Percutaneous coronary intervention surgery confirmed thrombus blockage in the middle segment of the right coronary artery, and the symptoms were relieved after thrombus removal.
Outcomes: The patient was discharged from the hospital on the 5th day after surgery without any recurrence of AMI up to now.
Lessons: The pharmacology and toxicity of batroxobin are intricate, necessitating careful consideration of potential secondary thrombosis during treatment, particularly regarding fibrinogen levels.
Keywords: acute myocardial infarction; batroxobin; fibrinogen; sudden sensorineural hearing loss; thrombosis.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of combining batroxobin with acupuncture treatment on hearing recovery in patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss.Acta Otolaryngol. 2024 Apr;144(4):299-305. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2024.2369295. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Acta Otolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 38953590
-
Prognostic predictors of sudden sensorineural hearing loss in defibrinogenation therapy.Acta Otolaryngol. 2016;136(3):271-6. doi: 10.3109/00016489.2015.1104723. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Acta Otolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 26573379 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of intratympanic corticosteroid, intravenous batroxobin and combined treatment for sudden sensorineural hearing loss with type-2 diabetes.Acta Otolaryngol. 2019 Jun;139(6):522-528. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2019.1592221. Epub 2019 Apr 22. Acta Otolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 31008670
-
Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A review focused on the contribution of vascular pathologies.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2024 Aug;51(4):747-754. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2024.05.009. Epub 2024 Jun 7. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2024. PMID: 38850720 Review.
-
Clinical management and progress in sudden sensorineural hearing loss during pregnancy.J Int Med Res. 2020 Feb;48(2):300060519870718. doi: 10.1177/0300060519870718. Epub 2019 Aug 27. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 31452412 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chau JK, Lin JR, Atashband S, Irvine RA, Westerberg BD. Systematic review of the evidence for the etiology of adult sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope. 2010;120:1011–21. - PubMed
-
- Kocak HE, Filiz Acipayam AS, Acipayam H, et al. . Microvascular dysfunction affects the development and prognosis of sudden idiopathic hearing loss. Clin Otolaryngol. 2017;42:602–7. - PubMed
-
- Akuter idiopathischer sensorineuraler Hörverlust – Steroidpulstherapie oder traditionelle orale Prednisolon-Therapie? Laryngorhinootologie. 2016;95:748–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

