The role of peritubular capillaritis in severity of lupus nephritis
- PMID: 40228478
- PMCID: PMC12123054
- DOI: 10.1177/09612033251335821
The role of peritubular capillaritis in severity of lupus nephritis
Abstract
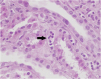
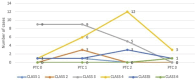
Background & ObjectivePresence of lupus nephritis is associated with a shorter time to death in systemic lupus erythematosus. The aim of this study was to determine the frequency of peritubular capillaritis (ptc) and its relationship with both active and chronic lesions in lupus nephritis.Material-MethodsSpecimens from 57 patients were re-evaluated. The degree of inflammation within the peritubular capillaries in each biopsy was assessed according to the Banff classification, and ptc scoring was performed. Additionally, patients were grouped based on high/low activity and chronicity index scores.ResultsForty-five (78.9%) of the patients were female, with a mean age of 27.43 years. Ptc was identified in 45 (78.9%) patients, with ptc scores of 1, 2, and 3 observed in 20 (35.08%), 20 (35.08%), and 5 (8.7%) patients, respectively. Severe ptc (scores 2 or 3) was more commonly detected in patients with elevated serum creatinine (>1.20 mg/dL) compared to those with normal creatinine levels (92.3% vs 29.5%, p < 0.001). The severity of ptc was higher in Class 4 patients than in Class 3 patients (68.2% vs 21.7%, p = 0.005). The rate of high ptc scores was greater in patients with an activity index of 6 or above compared to those with an activity index below 6 (62.5% vs 30.3%, p = 0.032). No significant correlation was found between the chronicity index and ptc.ConclusionsThe findings of this study suggest that ptc is a frequently observed pathological feature in patients with lupus nephritis. Furthermore, the severity of ptc appears to be positively associated with elevated serum creatinine levels, and higher ptc scores are more commonly detected in cases with a high activity index.
Keywords: Lupus nephritis; activity index; banff classification; peritubular capillaritis; renal outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Relation of peritubular capillary features to class of lupus nephritis.BMC Nephrol. 2016 Nov 9;17(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s12882-016-0388-2. BMC Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27829387 Free PMC article.
-
Diffuse Extent of Peritubular Capillaritis in Late Antibody-Mediated Rejection: Associations With Levels of Donor-Specific Antibodies and Chronic Allograft Injury.Transplantation. 2017 May;101(5):e178-e187. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001707. Transplantation. 2017. PMID: 28252564
-
The diffuse extent of peritubular capillaritis in renal allograft rejection is an independent risk factor for graft loss.Kidney Int. 2015 Aug;88(2):332-40. doi: 10.1038/ki.2015.64. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Kidney Int. 2015. PMID: 25738252
-
Peritubular capillaritis in renal allografts: prevalence, scoring system, reproducibility and clinicopathological correlates.Am J Transplant. 2008 Apr;8(4):819-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2007.02137.x. Epub 2008 Feb 5. Am J Transplant. 2008. PMID: 18261174
-
Peritubular capillary C4d deposition and renal outcome in post-transplant IgA nephropathy.Clin Transplant. 2007 Mar-Apr;21(2):159-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2007.00487.x. Clin Transplant. 2007. PMID: 17425739 Review.
References
-
- Alarcón GS. Multiethnic lupus cohorts: what have they taught us? Reumatol Clínica 2011; 7: 3–6. - PubMed
-
- Bastian HM, Roseman JM, McGwin G, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus in three ethnic groups. XII. Risk factors for lupus nephritis after diagnosis. Lupus 2002; 11: 152–160. - PubMed
-
- Cervera R, Khamashta MA, Font J, et al. Morbidity and mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus during a 5-year period. A multicenter prospective study of 1,000 patients. European Working Party on Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Medicine (Madr) 1999; 78: 167–175. - PubMed
-
- Anders H-J, Saxena R, Zhao M, et al. Lupus nephritis, Nat Rev Dis Primers 2020; 6: 7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

