STAT5B leukemic mutations, altering SH2 tyrosine 665, have opposing impacts on immune gene programs
- PMID: 40228864
- PMCID: PMC11999048
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202503222
STAT5B leukemic mutations, altering SH2 tyrosine 665, have opposing impacts on immune gene programs
Abstract
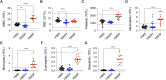
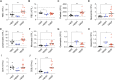
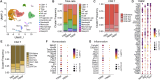
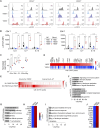
STAT5B is a vital transcription factor for lymphocytes. Here, the function of two STAT5B mutations from human T-cell leukemias: one substituting tyrosine 665 with phenylalanine (STAT5BY665F) and the other with histidine (STAT5BY665H), was interrogated. In silico modeling predicted divergent energetic effects on homodimerization with a range of pathogenicity. In primary T cells in vitro, STAT5BY665F showed gain-of-function, whereas STAT5BY665H demonstrated loss-of-function. Introducing the mutation into the mouse genome illustrated that the gain-of-function Stat5b Y665F mutation resulted in accumulation of CD8+ effector and memory and CD4+ regulatory T cells, altering CD8+/CD4+ ratios. In contrast, STAT5BY665H "knock-in" mice showed diminished CD8+ effector and memory and CD4+ regulatory T cells. In contrast to WT STAT5B, the STAT5BY665F variant displayed greater STAT5 phosphorylation, DNA binding, and transcriptional activity after cytokine activation, whereas the STAT5BY665H variant resembled a null. The work exemplifies how joining in silico and in vivo studies of single nucleotides deepens our understanding of disease-associated variants, revealing structural determinants of altered function, defining mechanistic roles, and, specifically here, identifying a gain-of-function variant that does not directly induce hematopoietic malignancy.
© 2025 Lee et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Update of
-
STAT5B leukemic mutations, altering SH2 tyrosine 665, have opposing impacts on immune gene programs.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 22:2024.12.20.629685. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.20.629685. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Life Sci Alliance. 2025 Apr 14;8(7):e202503222. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202503222. PMID: 39803507 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Andersson EI, Tanahashi T, Sekiguchi N, Gasparini VR, Bortoluzzi S, Kawakami T, Matsuda K, Mitsui T, Eldfors S, Bortoluzzi S, et al. (2016) High incidence of activating STAT5B mutations in CD4-positive T-cell large granular lymphocyte leukemia. Blood 128: 2465–2468. 10.1182/blood-2016-06-724856 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
