Inflammation and cancer cell survival: TRAF2 as a key player
- PMID: 40229245
- PMCID: PMC11997178
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-025-07609-w
Inflammation and cancer cell survival: TRAF2 as a key player
Abstract
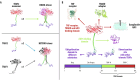
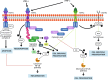
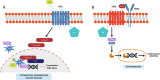
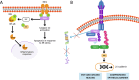
TNF receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2) plays a crucial role in both physiological and pathological processes. It takes part in the regulation of cell survival and death, tissue regeneration, development, endoplasmic reticulum stress response, autophagy, homeostasis of the epithelial barrier and regulation of adaptive and innate immunity. Initially identified for its interaction with TNF receptor 2 (TNFR2), TRAF2 contains a TRAF domain that enables homo- and hetero-oligomerization, allowing it to interact with multiple receptors and signaling molecules. While best known for mediating TNFR1 and TNFR2 signaling, TRAF2 also modulates other receptor pathways, including MAPK, NF-κB, and Wnt/β-catenin cascades. By regulating NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK), TRAF2 is a key activator of the alternative NF-κB pathway, linking it to inflammatory diseases, immune dysfunction, and tumorigenesis. In the innate immune system, TRAF2 influences macrophage differentiation, activation, and survival and stimulates natural killer cell cytotoxicity. In the adaptive immune system, it represses effector B- and T-cell activity while sustaining regulatory T-cell function, thus promoting immune suppression. The lack of fine-tuning of TRAF2 activity leads to excessive NF-kB activation, driving chronic inflammation and autoimmunity. Although TRAF2 can act as a tumor suppressor, it is predominantly described as a tumor promoter, as its expression has been correlated with increased metastatic potential and poorer prognosis in several types of cancer. Targeting TRAF2 or TRAF2-dependent signaling pathways might represent a promising anti-cancer therapeutic strategy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Noonan DM, De Lerma Barbaro A, Vannini N, Mortara L, Albini A. Inflammation, inflammatory cells and angiogenesis: decisions and indecisions. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008;27:31–40. 10.1007/s10555-007-9108-5. - PubMed
-
- Speeckaert MM, Speeckaert R, Laute M, Vanholder R, Delanghe JR. Tumor necrosis factor receptors: biology and therapeutic potential in kidney diseases. Am J Nephrol. 2012;36:261–70. 10.1159/000342333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

