Cost-effectiveness of CDK4/6 inhibitors for second-line HR+/HER2- advanced or metastatic breast cancer in China
- PMID: 40229346
- PMCID: PMC11997058
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-97504-3
Cost-effectiveness of CDK4/6 inhibitors for second-line HR+/HER2- advanced or metastatic breast cancer in China
Abstract
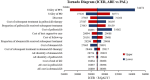
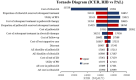
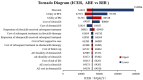
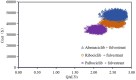
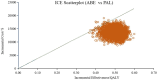
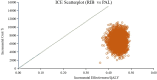
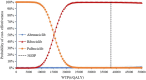
Hormone receptor HR-positive/HER2-negative (HR+/HER2-) breast cancer is the most common subtype in China, representing 60-70% of cases, with a rising incidence due to aging demographics and lifestyle changes. CDK4/6 inhibitors such as palbociclib, ribociclib and abemaciclib have been proven effective in treating HR+/HER2 - advanced or metastatic breast cancer (ABC/MBC), though they may increase healthcare costs. This study aims to compare the efficacy, safety and cost-effectiveness of CDK4/6 inhibitors for the second-line treatment of HR+/HER2 - ABC/MBC from the Chinese healthcare perspective. A cohort-based partitioned survival model was utilized, drawing on the survival data published from PALOMA-3, MONALEESA-3 and MONARCH-2 trials. Costs, and quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) were used to calculate the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) over a 15-year time horizon. Deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses were performed to assess the robustness of the model results. In the base-case analysis, the model estimated health benefits to be 2.10 QALYs for palbociclib plus fulvestrant (PAL + FUL), 2.55 QALYs for ribociclib plus fulvestrant (RIB + FUL), and 2.60 QALYs for abemaciclib plus fulvestrant (ABE + FUL), with corresponding costs of $34,423, $41,119, and $48,019. Compared with PAL + FUL, the ICERs were $27,161 per QALY for ABE + FUL and $15,073 per QALY for RIB + FUL. The robustness of these findings was confirmed through uncertainty analyses. Among the three strategies, the most cost-effective probabilities of PAL + FUL, RIB + FUL and ABE + FUL were 0%, 99.8%, and 0.2% under the willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold of 3 times per-capita gross domestic product ($37,738) in China. This study indicated that both RIB + FUL and ABE + FUL are cost-effective at the WTP threshold compared with PAL + FUL. Notably, RIB + FUL offers the greatest cost-effective advantage for the second-line treatment of HR+/HER2 - ABC/MBC among these three CDK4/6 inhibitors.
Keywords: Breast cancer; CDK4/6 inhibitors; China; Cost-effectiveness; Fulvestrant; HR-positive/HER2-negative.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: The data of the PFS/OS was based on previously published trials, and ethics approval or specific consent procedures were not applicable for this study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness of CDK4/6 inhibitors in HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Curr Med Res Opin. 2024 Oct;40(10):1753-1767. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2024.2402074. Epub 2024 Sep 21. Curr Med Res Opin. 2024. PMID: 39305463
-
Real-world effectiveness comparison of first-line palbociclib, ribociclib or abemaciclib plus endocrine therapy in advanced HR-positive/HER2-negative BC patients: results from the multicenter PALMARES-2 study.Ann Oncol. 2025 Jul;36(7):762-774. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2025.03.023. Epub 2025 Apr 8. Ann Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40204155
-
Cost-Effectiveness of Ribociclib plus Letrozole Versus Palbociclib plus Letrozole and Letrozole Monotherapy in the First-Line Treatment of Postmenopausal Women with HR+/HER2- Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer: A U.S. Payer Perspective.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018 Jun;24(6):514-523. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2018.24.6.514. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018. PMID: 29799329 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world evidence from Japan regarding survival outcomes and treatment sequence in patients receiving CDK4/6 inhibitor plus endocrine therapy as first- or second-line treatment for hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer.Breast Cancer. 2025 Jul;32(4):841-856. doi: 10.1007/s12282-025-01713-7. Epub 2025 May 20. Breast Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40392524 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(45):iii-iv, ix-221. doi: 10.3310/hta11450. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999840
Cited by
-
CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer therapy: mechanisms of drug resistance and strategies for treatment.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 12;16:1549520. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1549520. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40421216 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bray, F. A. O. et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J. Clin.74, 1542–4863. 10.3322/caac.21834 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Fan, L. et al. Breast cancer in China. Lancet Oncol.15, e279–289. 10.1016/s1470-2045(13)70567-9 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Hamilton, E. & Infante, J. R. Targeting CDK4/6 in patients with cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev.45, 129–138. 10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.03.002 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

