Alveolar cleft reconstruction using autogenous double iliac corticocancellous bone blocks technique versus particulate autogenous spongy bone graft from anterior iliac crest
- PMID: 40229452
- PMCID: PMC11996971
- DOI: 10.1007/s00784-025-06288-3
Alveolar cleft reconstruction using autogenous double iliac corticocancellous bone blocks technique versus particulate autogenous spongy bone graft from anterior iliac crest
Abstract
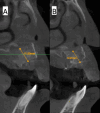
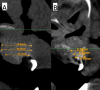
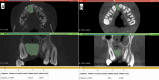
Objective: The primary goals for alveolar cleft grafting are to gain and maintain bone in the cleft area that provides continuity for the maxillary segments, allowing the stability of the maxilla and building the bony foundation for the erupting cleft teeth and closure of the oronasal communication. The current study compared the effectiveness of the double iliac corticocancellous bone blocks technique versus the particulate autogenous spongy bone graft from the anterior iliac crest in alveolar cleft grafting in the mixed dentition stage.
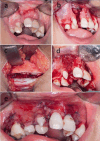
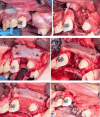
Patients and methods: The current randomized clinical study included 18 patients with unilateral alveolar clefts. They were divided into two equal groups according to the technique used for grafting; group (1) included nine patients in whom grafting with double iliac corticocancellous bone blocks with cancellous bone particulates in between was used (study group), and group (2) included nine patients in whom conventional cancellous particulate bone grafting from anterior iliac crest was used (Control group).
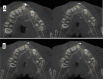
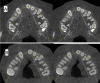
Results: Nine months postoperatively, the study group showed superior results regarding graft width, height, and volume compared to the control group in the current study.
Conclusion: Regarding the graft success factors represented by the maintained graft labio-palatal width, graft height, and total graft volume, the technique of double iliac corticocancellous bone blocks was markedly effective in reconstructing alveolar clefts when compared with the conventional grafting technique that utilized cancellous particulate bone alone from the anterior iliac crest.
Clinical relevance: The double iliac corticocancellous bone blocks technique maintained the grafted bone volume, width, and height.
Keywords: Anterior iliac crest; Double iliac corticocancellous bone blocks; Iliac cancellous bone graft; Phase of mixed dentition; Secondary alveolar cleft bone grafting.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was conducted following the Declaration of Helsinki's guidelines for medical research, and the research ethics committee of Cairo University's Faculty of Dentistry provided a clarification letter. All participants that were included in the study signed a written informed consent. Publication consent: The authors affirm that all research participants and/or their guardians signed informed consent for the publication of the images. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Dao AM, Goudy SL (2016) Cleft palate repair, gingivoperiosteoplasty, and alveolar bone grafting. Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics 24(4):467–476 - PubMed
-
- Boyne PJ, Sands NR (1976) Combined orthodontic-surgical management of residual palato-alveolar cleft defects. Am J Orthod 70(1):20–37 - PubMed
-
- Swan MC, Goodacre TEE (2006) Morbidity at the iliac crest donor site following bone grafting of the cleft alveolus. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 44(2):129–133 - PubMed
-
- Marukawa E, Oshina H, Iino G, Morita K, Omura K (2011) Reduction of bone resorption by the application of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in bone grafting of the alveolar cleft. Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery 39(4):278–283 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

